Greenhouse Gases Effect
Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube
Enhanced Greenhouse Gas Effect Greenhouse Effect
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
The Greenhouse Effect
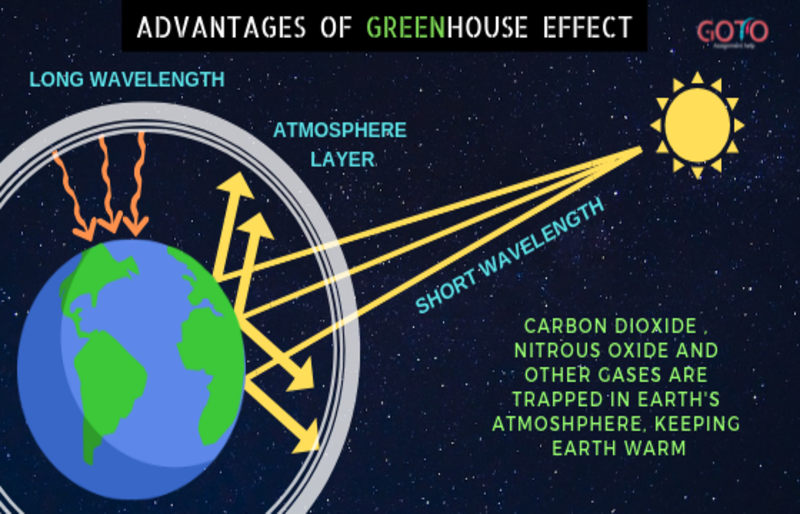
The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases
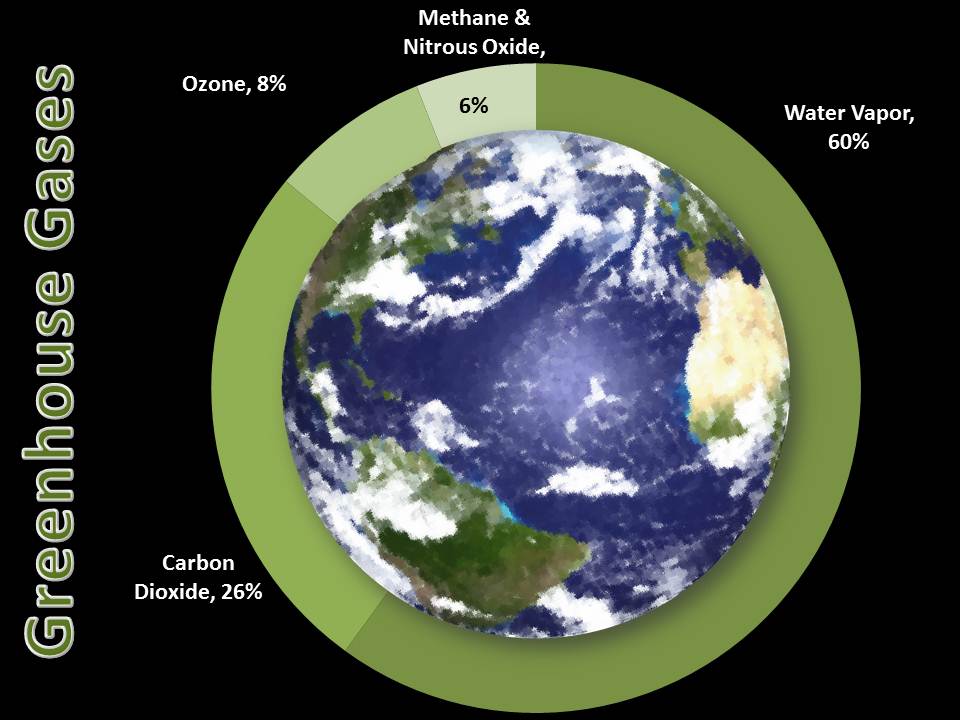
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
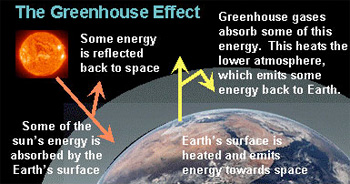
This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere.

Greenhouse gases effect. The trapped heat warms the greenhouse. NASA documents the greenhouse effect. Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes.
An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect. Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules. Greenhouse gases warm the planet.
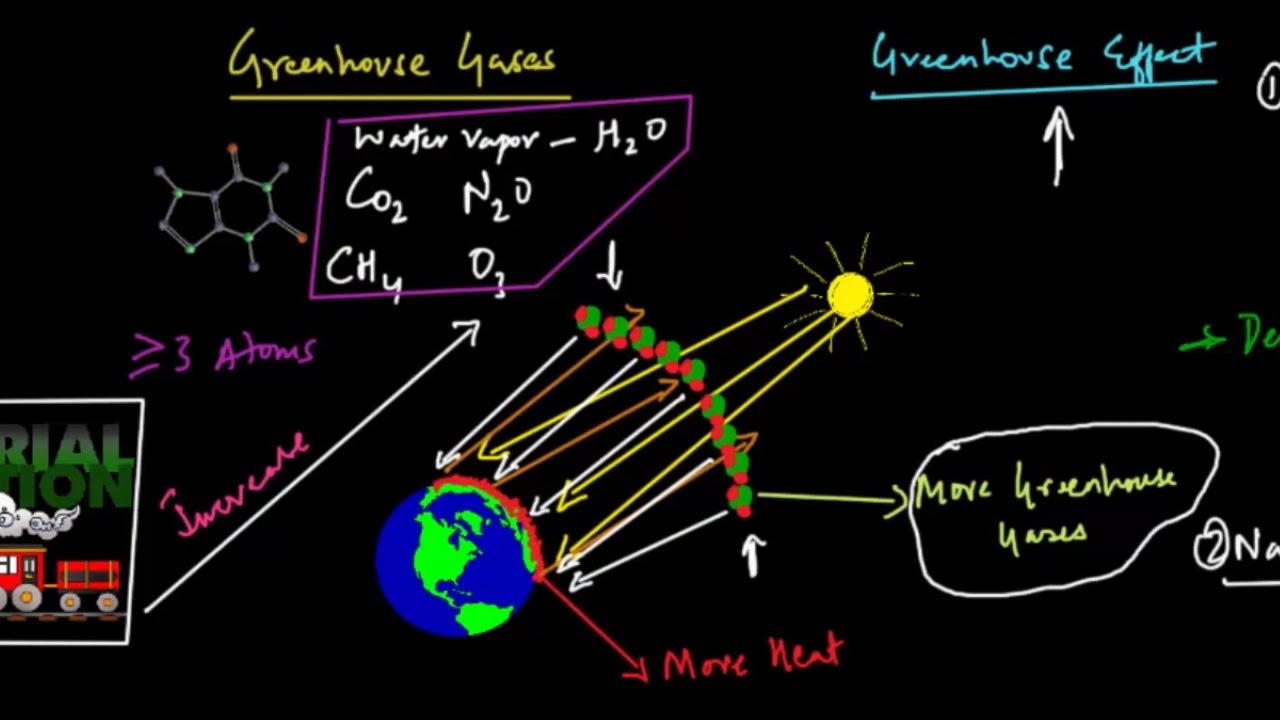
Some gases in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases, because they have a greenhouse effect on Earth. The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane. This trapped heat helps in controlle.
Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made. Greenhouse gases have far-ranging environmental and health effects. Contributors to Greenhouse Effect Those gas molecules in the Earth's atmosphere with three or more atoms are called "greenhouse gases" because they can capture outgoing infrared energy from the Earth, thereby warming the planet.
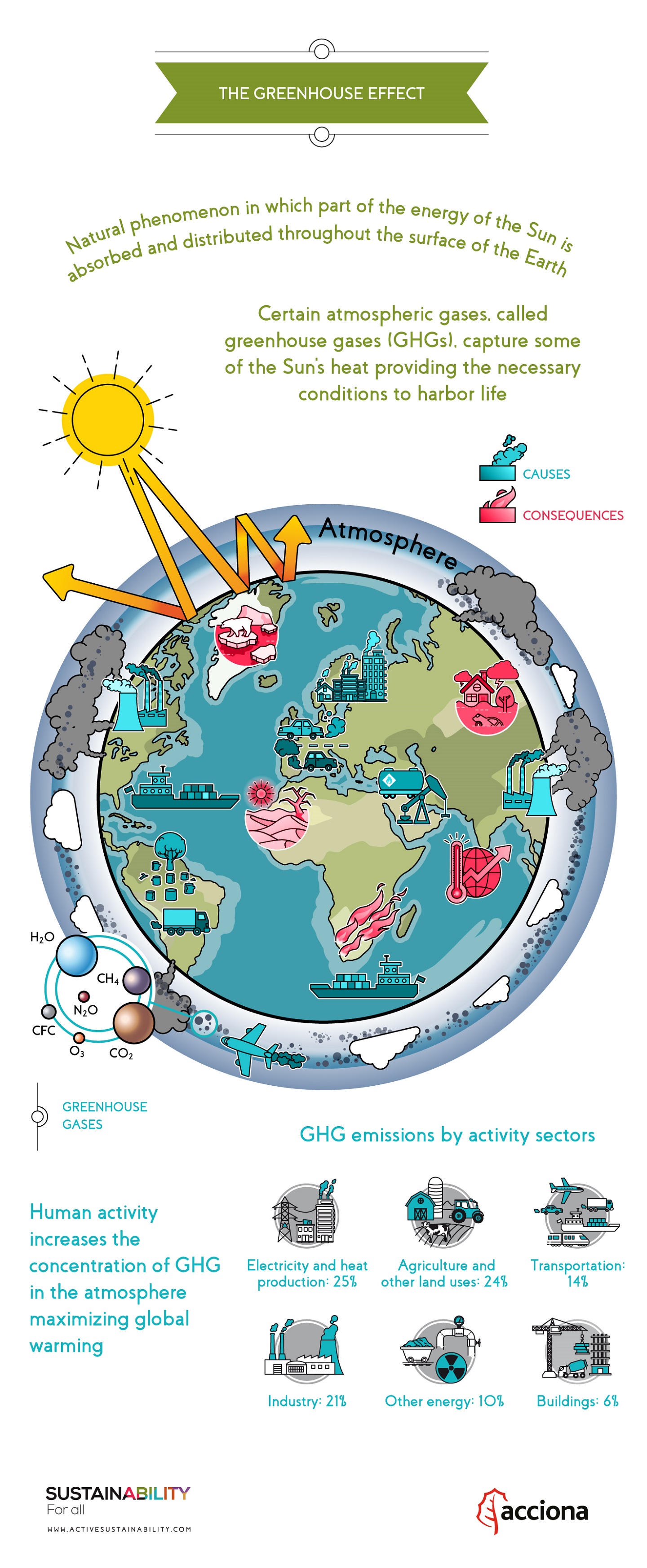
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in the Earth's atmosphere.Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases. Five Major Greenhouse Gases. Help Earth get rid of the excess greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases are a hot topic (pun intended) when it comes to global warming. Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, warming it. The Earth's surface absorb the sunlight’s energy.
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. What greenhouse gases do humans generate?. Greenhouse gases are the main source of air pollution and include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and sulphur hexafluoride.
We need some greenhouse gases. Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%). A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto the Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to live. Scientists call the tiny particles ‘black carbon’ (you call it soot or smoke) and attribute their warming effect to the fact that the resulting layer of black particles in the lower atmosphere absorbs heat.
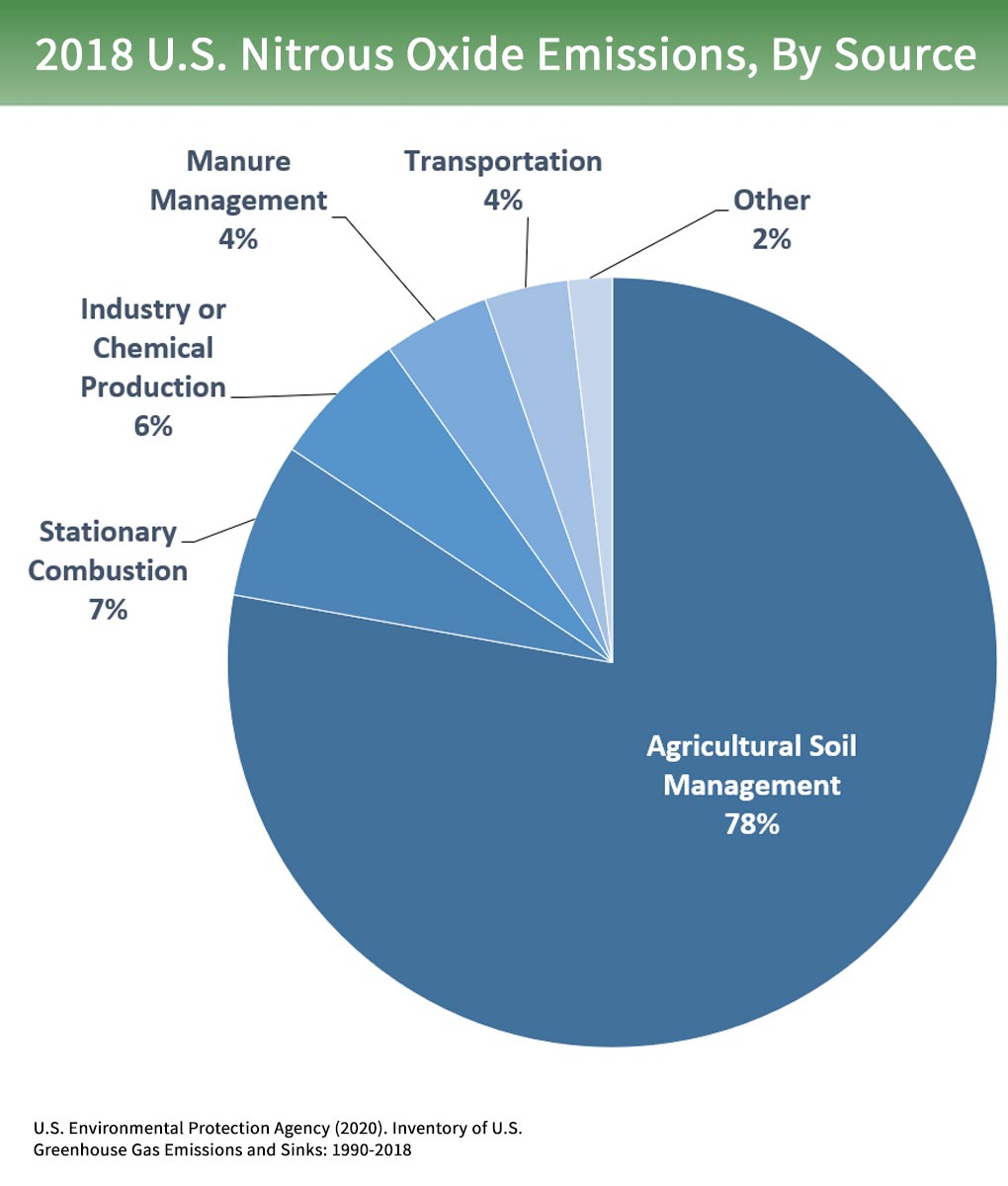
This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution., coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips. How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work?. Human activity increases the concentration of greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere maximizing global warming.
Our activities produce four major greenhouse gases (Figure 1). A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight. In computer-based models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time.
Despite all the talk about carbon capture, carbon footprints and carbon trading, carbon dioxide only causes nine to 26 percent of the greenhouse effect. The intensity of the downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – will depend on the atmosphere's temperature and on the amount of. "The difference in an atmosphere with a strong water vapor feedback and one with a weak feedback is enormous," Dessler said.
However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. NASA Video 1 and NASA Video 2. These greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO 2, methane, nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and.
For eg., carbondioxide and chlorofluorocarbons.” Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation, etc. The greenhouse effect is when carbon dioxide and other gases in the Earth's atmosphere capture the Sun's heat radiation. For more videos go to:.
The greenhouse effect helps earth maintain a decent temperature that makes this planet habitable. Then compare to the effect of glass panes. The greenhouse gases include water vapor with three atoms (H2O), ozone (O3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4).
Interaction with factories, agriculture, and cars. The net effect is the gradual heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface, a process known as global warming. As more greenhouse gases are pumped into the atmosphere, however, the temperature increases and there's a risk of creating feedback effects that could make the Earth warmer still.
This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases.This is called the "greenhouse effect".Most greenhouse gases are natural - water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth. Let's learn all about greenhouse effect today. By increasing the heat in the.
They also include small but lethal amounts of hydrofluorocarbons and perfluorocarbons. The "greenhouse effect" is the effect of atmospheric gases like carbon dioxide absorbing energy from the sun and earth and "trapping" it near the Earth's surface, warming the Earth to a temperature range that is hospitable for life. NASA satellites show how the greenhouse effect boosted by human action contributes to global warming:.
While all greenhouse gases (GHG) have a warming effect on our planet, this warming effect is not equivalent across all GHG. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would not support most forms of life. That means that the majority of warming.
Scientists call these gases “greenhouse gases” (GHGs) because they act like the wrong way reflective glass in our global greenhouse. The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
If not for any greenhouse gas, Earth would be too cold. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions.
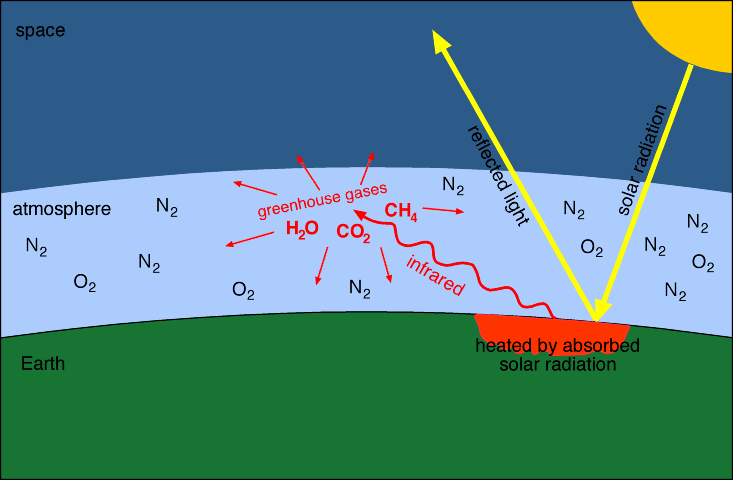
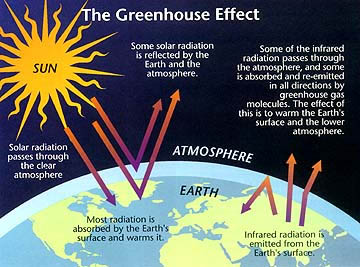
Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth. Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change. Greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which thermal radiation from earth’s surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directions.
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. The increase in CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion was a result of multiple factors, including increased energy use due to greater heating and cooling needs due to a colder winter and hotter summer in 18 compared to 17. The clear effect of the greenhouse gases is the stable heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface, thus, global warming.
These gases behave differently in the atmosphere and their long-term effects on climate change vary. The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. That sunlight creates warmth.
Every day we generate greenhouse gases through. They get their name from greenhouses. Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties.
The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn’t let that warmth escape. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 30 percent.
Water vapor feedback can also amplify the warming effect of other greenhouse gases, such that the warming brought about by increased carbon dioxide allows more water vapor to enter the atmosphere. The major factor contributing to a GHG warming effect is whether it is a stock or flow gas. Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat.
The Greenhouse Gas Effect. The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. It is, in part, a natural process.
Greenhouse gases reflect heat radiation that the Earth emits, and stop it from being lost into space. While some gases are produced through natural processes like animal and plant respiration, human activity such as fossil fuel burning, livestock rearing and vehicle emissions have increased their quantity. Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet.
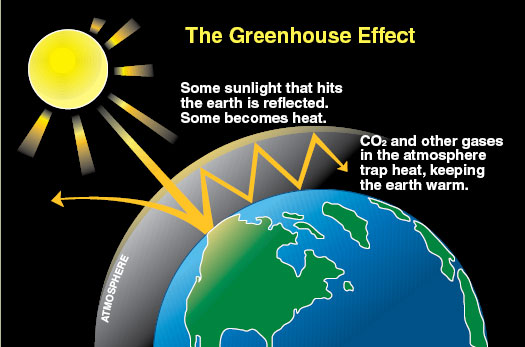
It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experiences because greenhouse gases trap energy from the sun.
Long-lived gases that remain semi-permanently in the atmosphere and do not respond physically. But too much greenhouse gas can make it too hot. Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global human-caused. The entire credit for this inhabiting temperature goes to the greenhouse gases.
These gases absorb heat energy emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiate it back to the ground. It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun. Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, passing through the blanket of greenhouse gases.
Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space. Burning of fossil fuelsand deforestationleading to higher carbon dioxide concentrations in the air. Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities.
Have a Greenhouse Gas Attack!. Updated February 11, 17 | Infoplease Staff. While the greenhouse effect is an essential environmental prerequisite for life on Earth, there really can be too much of a good thing.
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid- th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. The gases that help capture the heat, called “greenhouse gases,“ include. That’s exactly how greenhouse gases act.
The problems begin when human activities distort and accelerate the natural process by creating moregreenhouse gases in the atmosphere than are necessary to warm the planet to an ideal temperature. Greenhouse gases include CO2, water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides.
What happens when you add clouds?. The greenhouse effect causes some of this energy to be waylaid in the atmosphere, absorbed and released by greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gas emissions increased compared to 17 levels.
The ability of certain gases, greenhouse gases, to be transparent to inbound. People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors:. Some of the major green house gases are.
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth’s atmosphere. “Greenhouse gases are the gases that absorb the infrared radiations and create a greenhouse effect. This is called the "greenhouse effect." Up to a point, the greenhouse effect helps keep the Earth at a temperature suitable for life.
Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping. The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following:. Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process by which some of the radiant heat from the Sun is captured in the lower atmosphere of the Earth, thus maintaining the temperature of the Earth's surface. The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere. They cause climate change by trapping heat, and they also contribute to respiratory disease from smog and air pollution.
In this way, they contribute to the greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet from losing all of its heat from the surface at night. Once absorbed, this energy is sent back into the atmosphere. Incidence of the human being in the greenhouse effect.
Other greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer. In a greenhouse, the sun's heat can come in but cannot go out.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where atmospheric gases trap heat – a phenomena that allows the Earth to retain enough solar heat to be livable. Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth’s temperature over geologic time. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist.
The main sources of greenhouse gases due to human activity are:. These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?.
Livestock enteric fermentationand manure management,97paddy ricefarming, land use and wetland changes, man-made. From 1990 to 15, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth’s atmosphere increased by 37 percent. Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through.
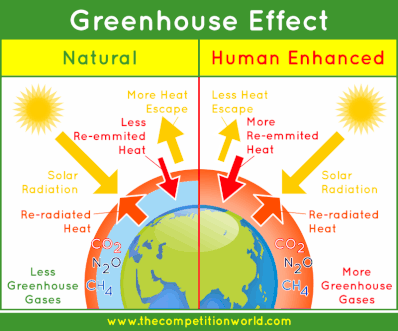
4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
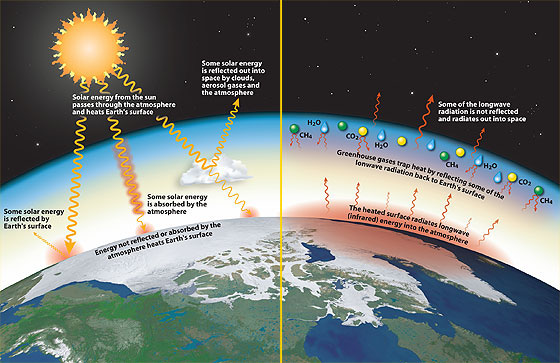
Too Much Of A Good Thing

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5440 Science Photo Library

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids

Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Iasmania Civil Services Preparation Online Upsc Ias Study Material

Global Warming Schools

What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
.png)
Greenhouse Effect Energy Education

2c Explore The Greenhouse Effect

The Greenhouse Effect World101

Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

Misconception Monday Is Greenhouse Misleading National Center For Science Education

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids

15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases

Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram
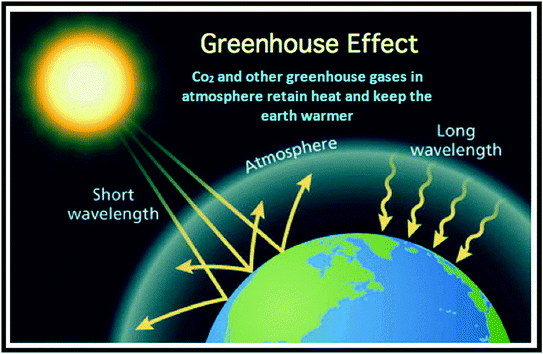
Reducing The Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases Springerlink

2c Explore The Greenhouse Effect
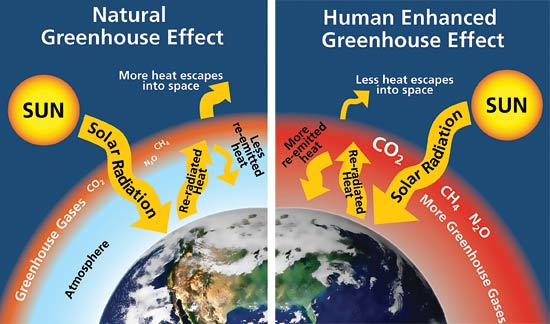
How Is The Greenhouse Effect Related To Global Warming Socratic

Team Braunschweig Project Content 14 Igem Org

The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education

Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Priyamstudycentre

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
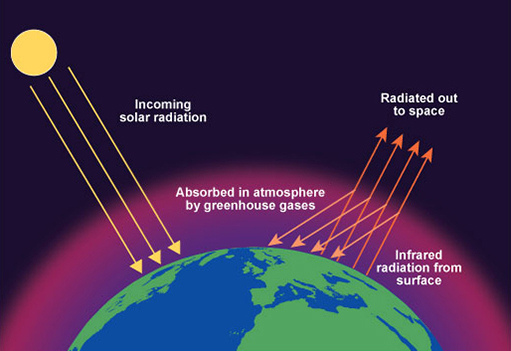
Week 7 The Special Ones 2 2 The Greenhouse Effect Openlearn Open University Exo 1

Global Warming Impact On Greenhouse Gases Ag Decision Maker
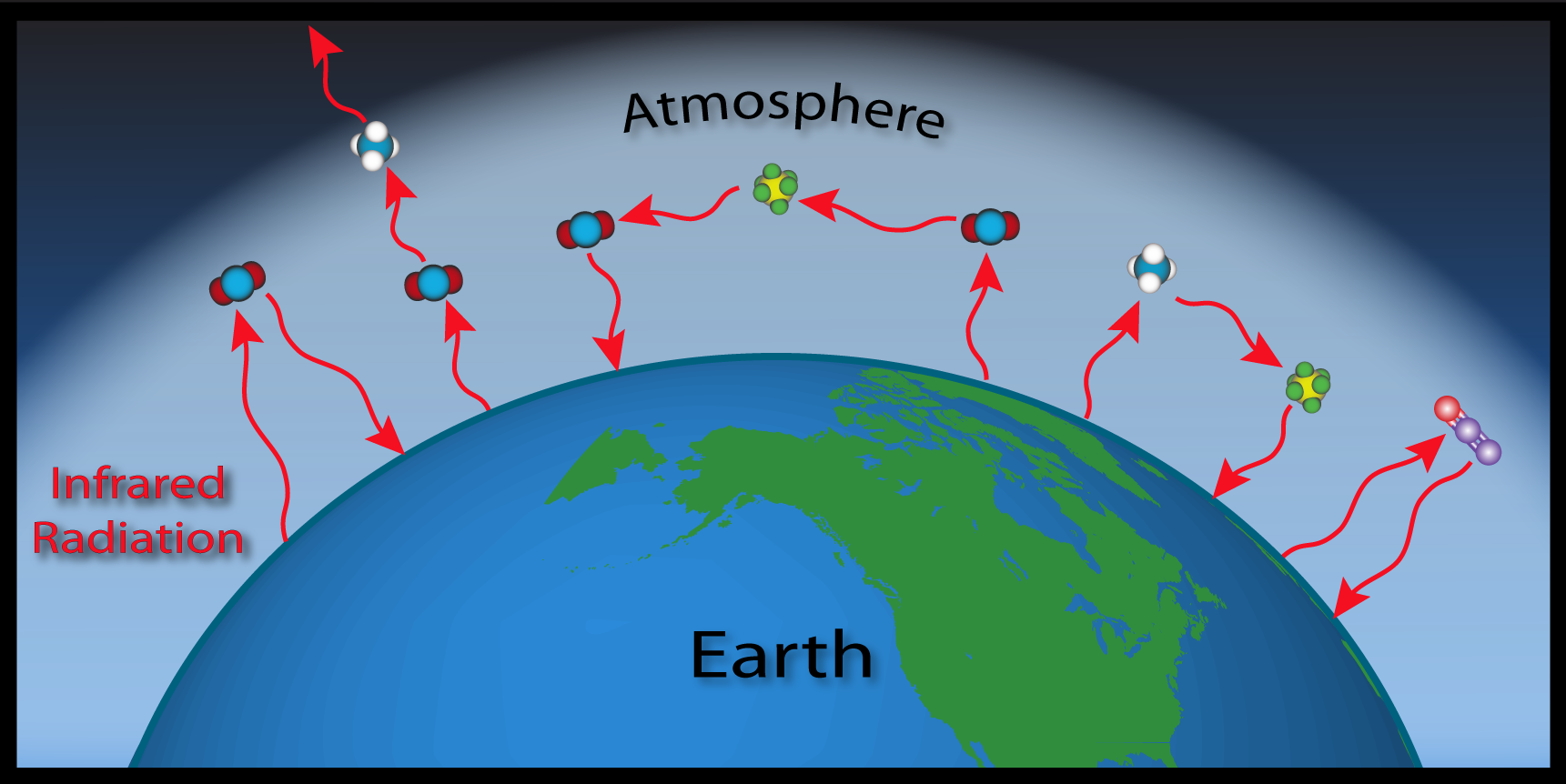
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Pin By Edson Chongore On Architecture Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect

3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network

Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
Clim2b Greenhouse Gas Effect Sources Worksheet Answers
The Greenhouse Effect
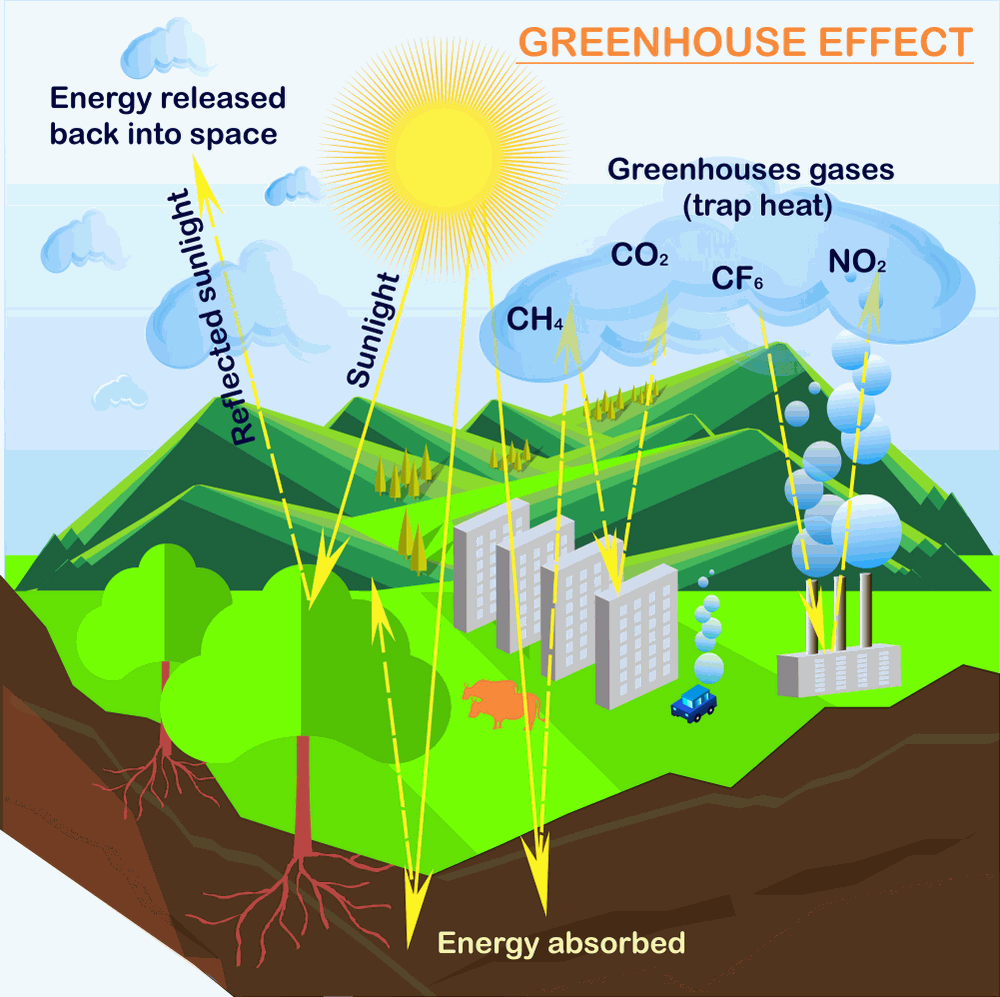
What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19

Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Greenhouse Gases

Warm On Top Cold Below Unexpected Greenhouse Gas Effect In Lakes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)
Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy
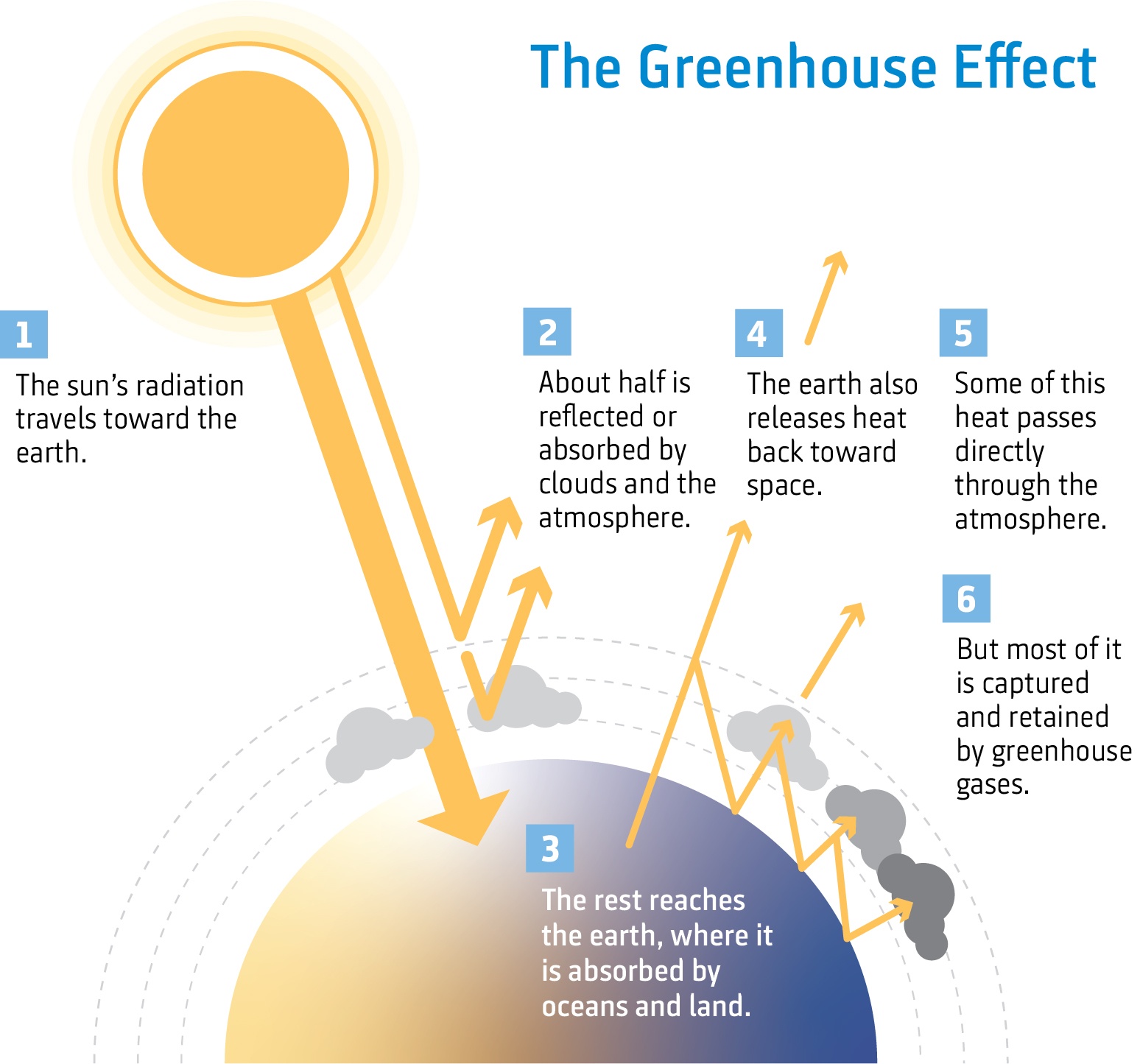
Climate Change The Science Niwa
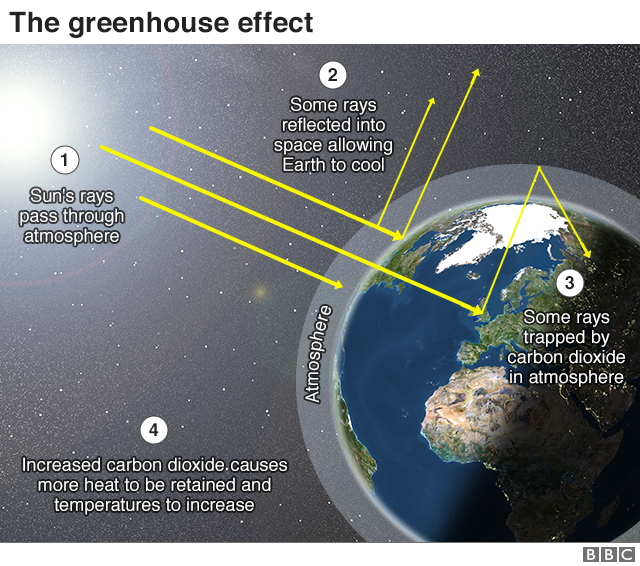
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
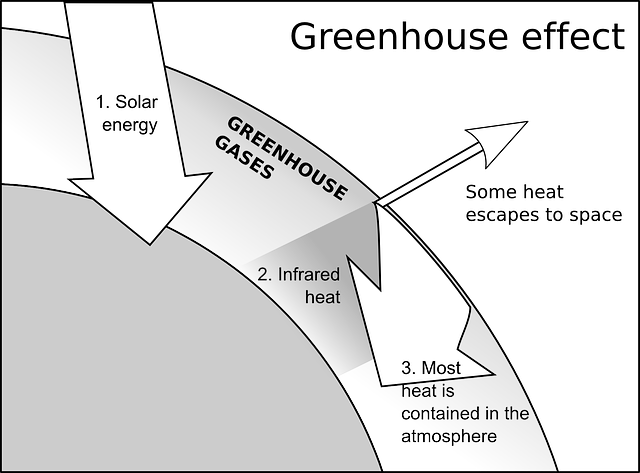
What Is Greenhouse Effect And What Are Greenhouse Gases Earth Eclipse

The Greenhouse Effect Explained
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect

How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
Volcanoes Greenhouse Gases And Temperature Change
What Is The Greenhouse Effect

Solved 1 Explain How The Greenhouse Effect Works Use Ex Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsms9bocgmr3uwu1eitzch9cq8fm0mu Abd6j S1iyhbe3oclxn Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcql3boteov9mpuolxv9uln6x4jzfoqjgo6imcjs3rs Usqp Cau
Untitled Document

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
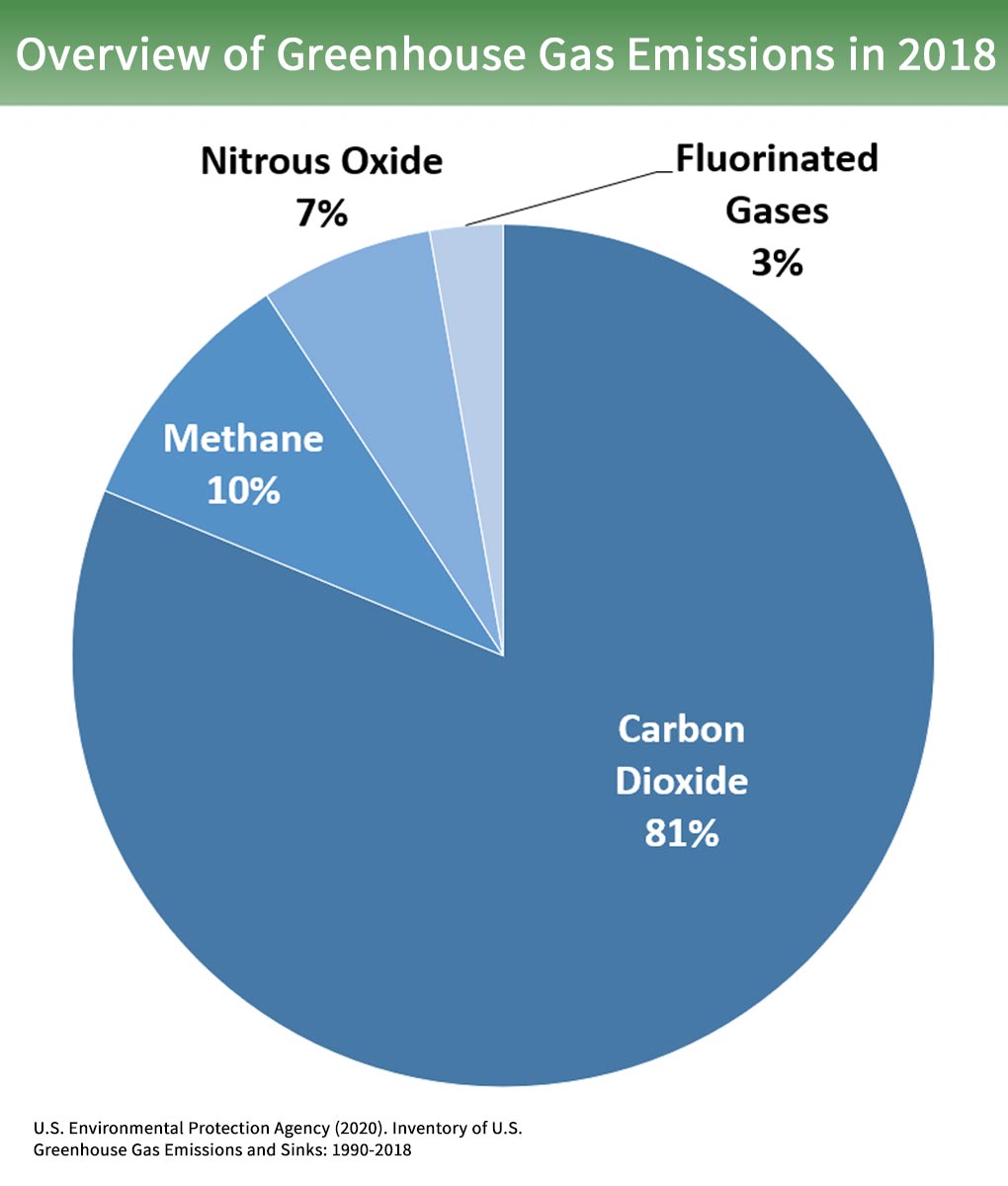
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood

The Greenhouse Effect World101

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future

Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube

Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5478 Science Photo Library

Issue 22 The Problem With Cow Farts Reachout Reporter
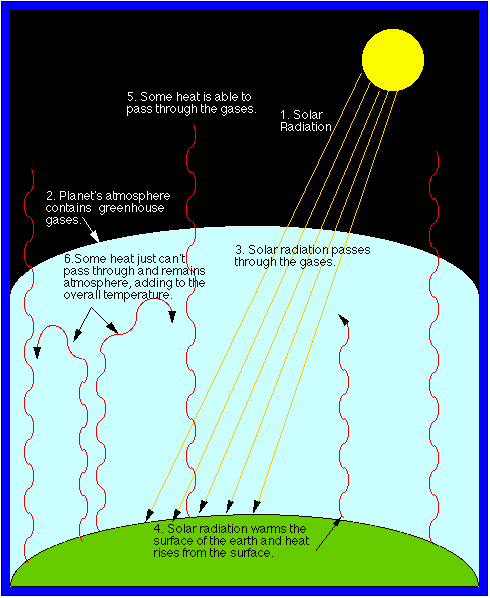
Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gases Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia

Greenhouse Effect
Q Tbn 3aand9gcswtw6jmpki0thvbw9s03clyicmq0e Etfhbtsrvhxuoxvo5xud Usqp Cau

5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica

How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut

The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks
3
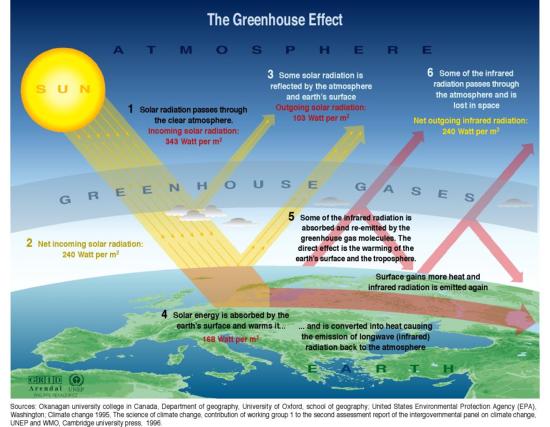
Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal
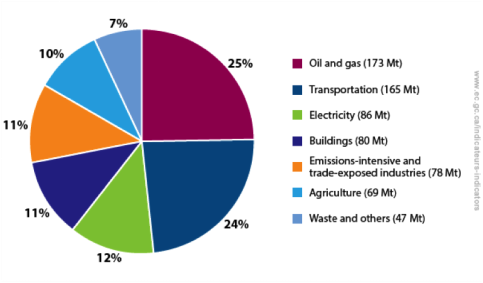
Effects Greenhouse Effect

Greenhouse Effect Blog Nigurha Com Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
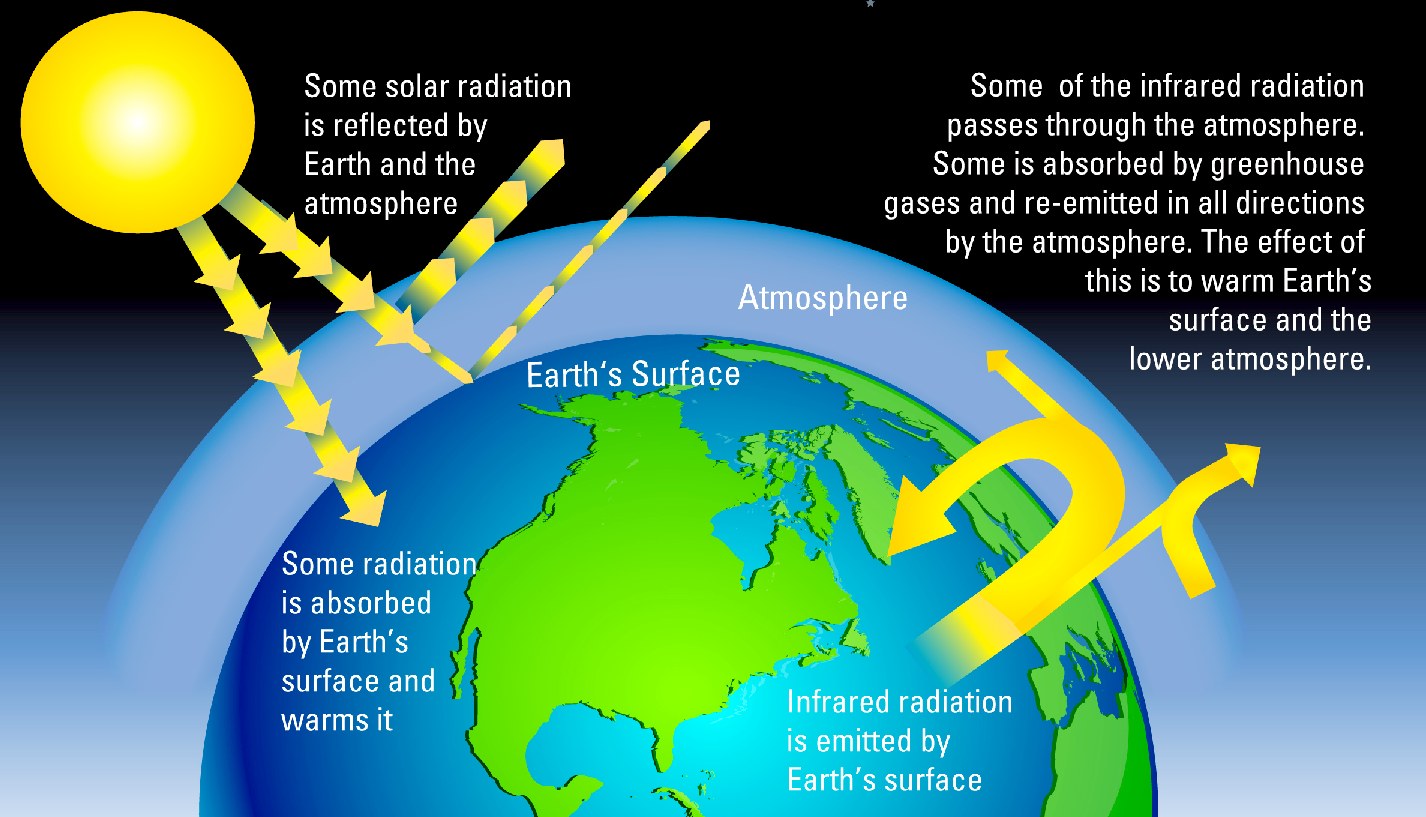
Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Aluminium For Future Generations Greenhouse Gases

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Chemistry Byju S
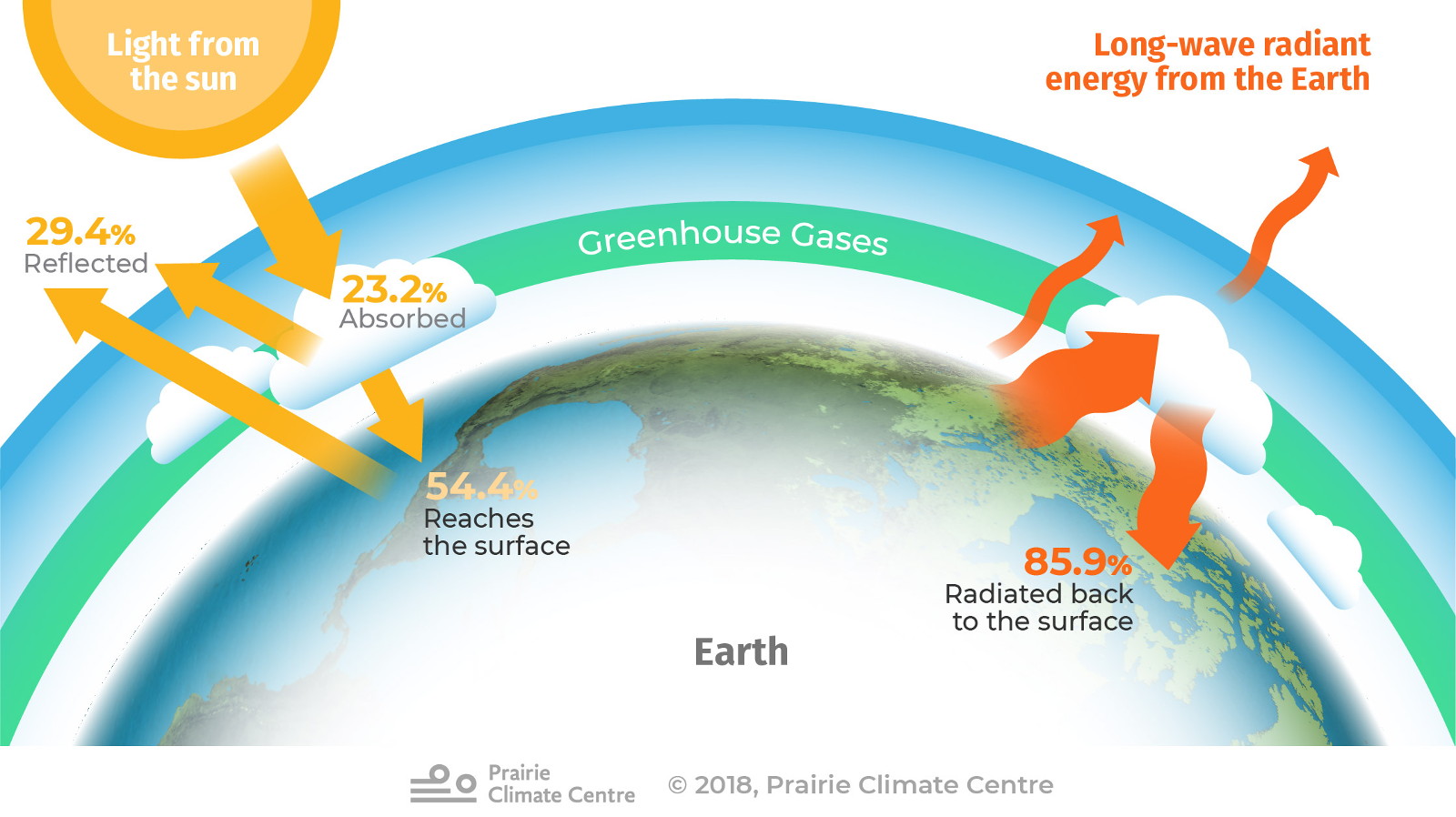
Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada

What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly

Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
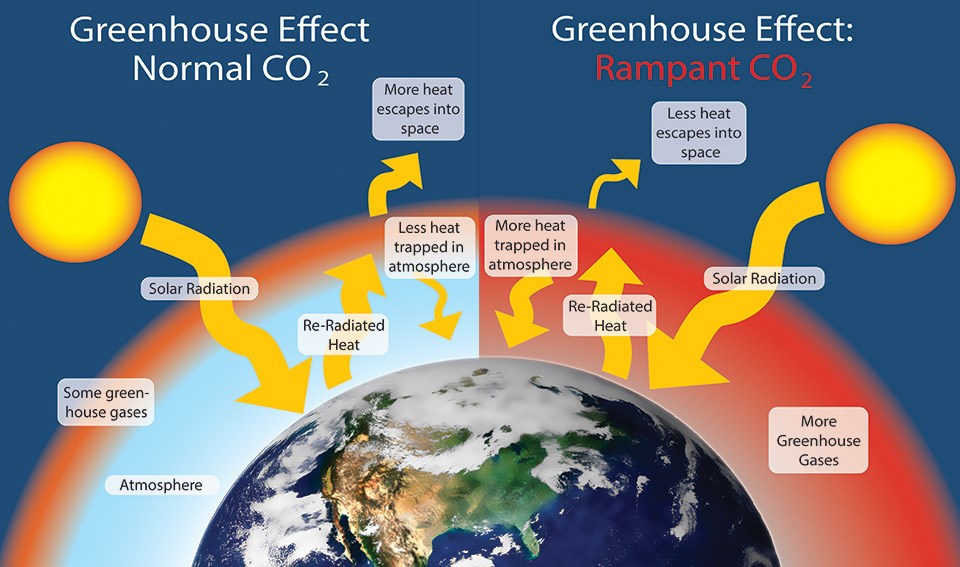
What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service

What Are The Greenhouse Gases Infographic 360training

Diagram Of The Greenhouse Gas Effect Download Scientific Diagram

Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
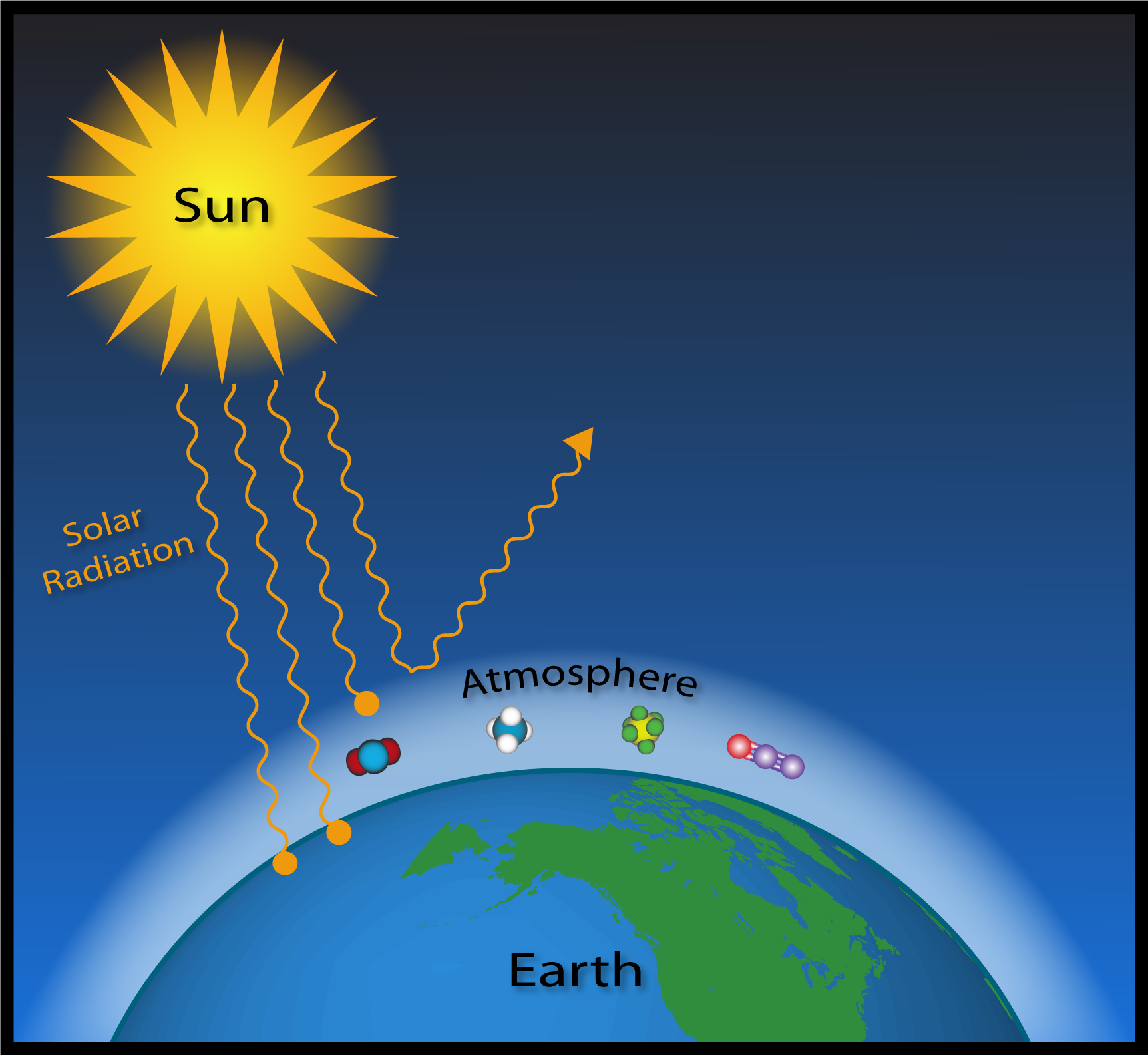
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
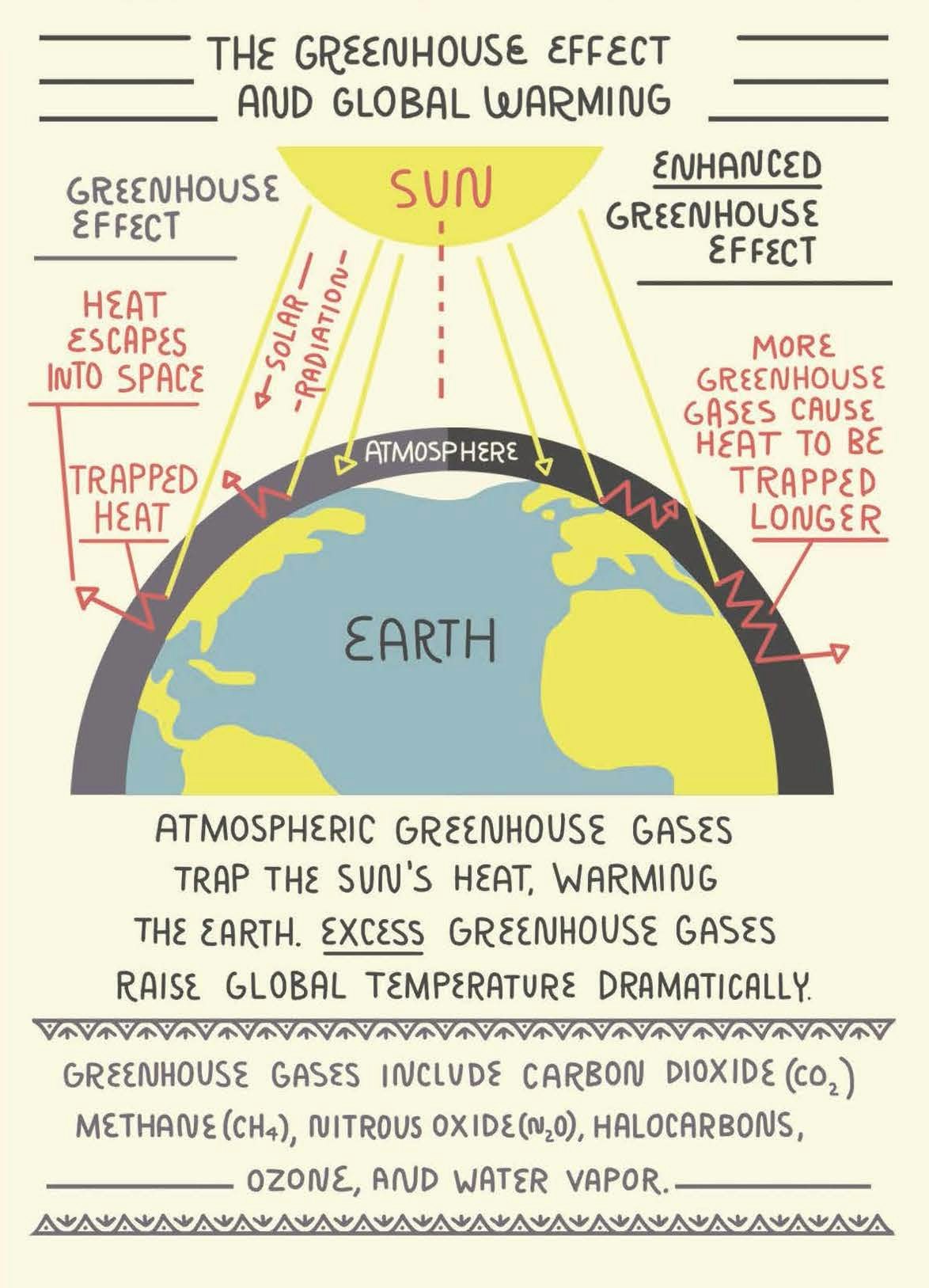
What Is The Greenhouse Effect And How Does It Cause Global Warming
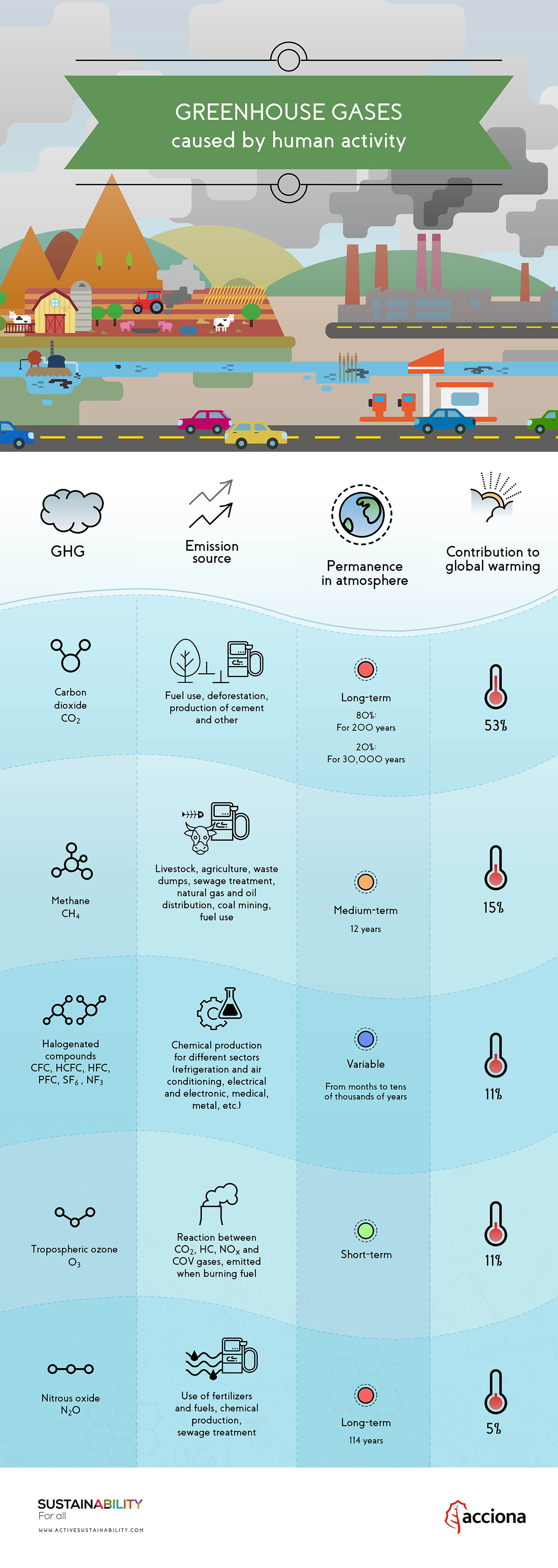
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects

Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Which Of These Is Not A Greenhouse Gas Co2 Methane So2 Or Cfc Quora
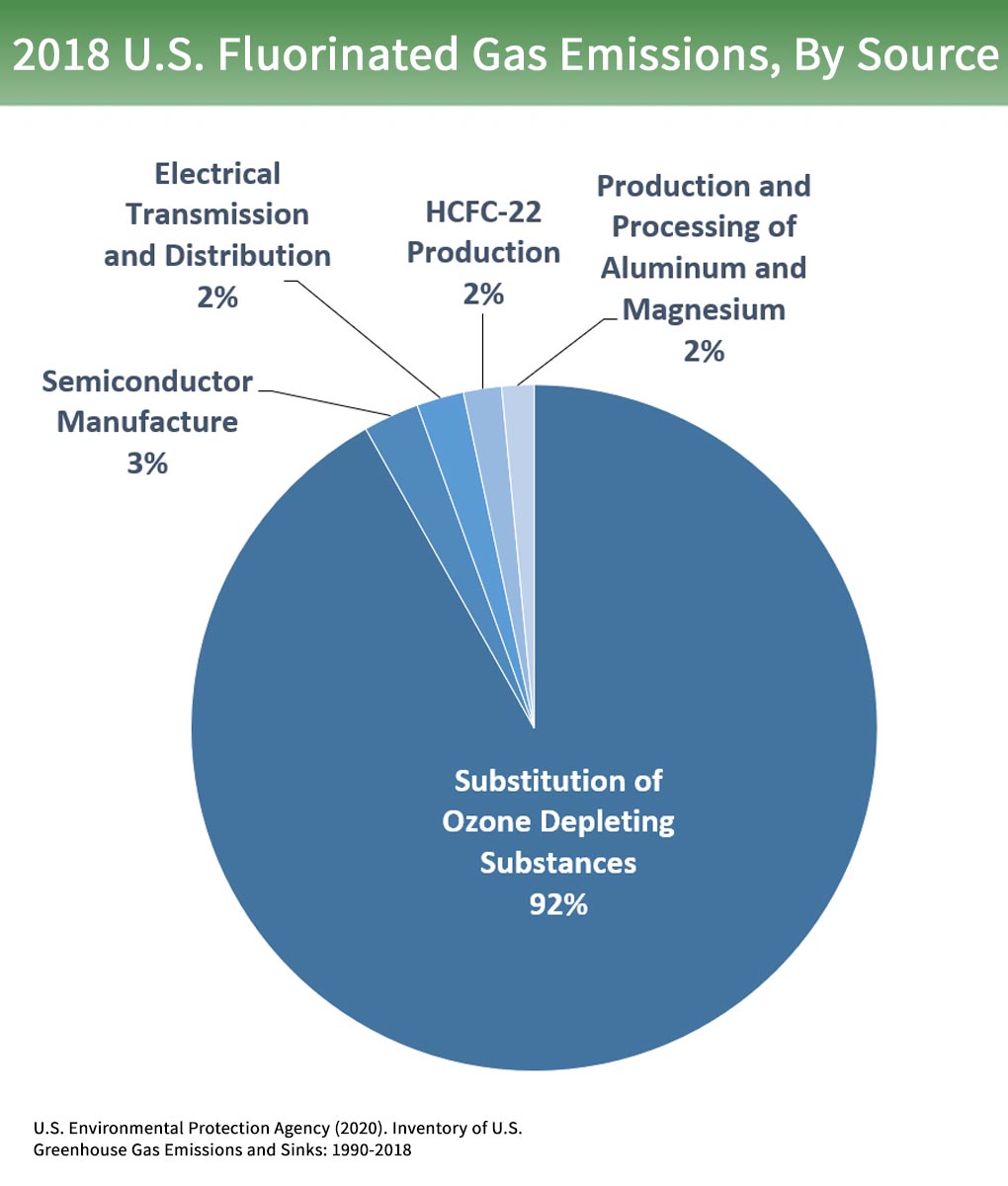
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know

What Are Greenhouse Gases Main Sources And Climate Impact

Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization

Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



