Greenhouse Gas Definition Chemistry

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

The Greenhouse Effect
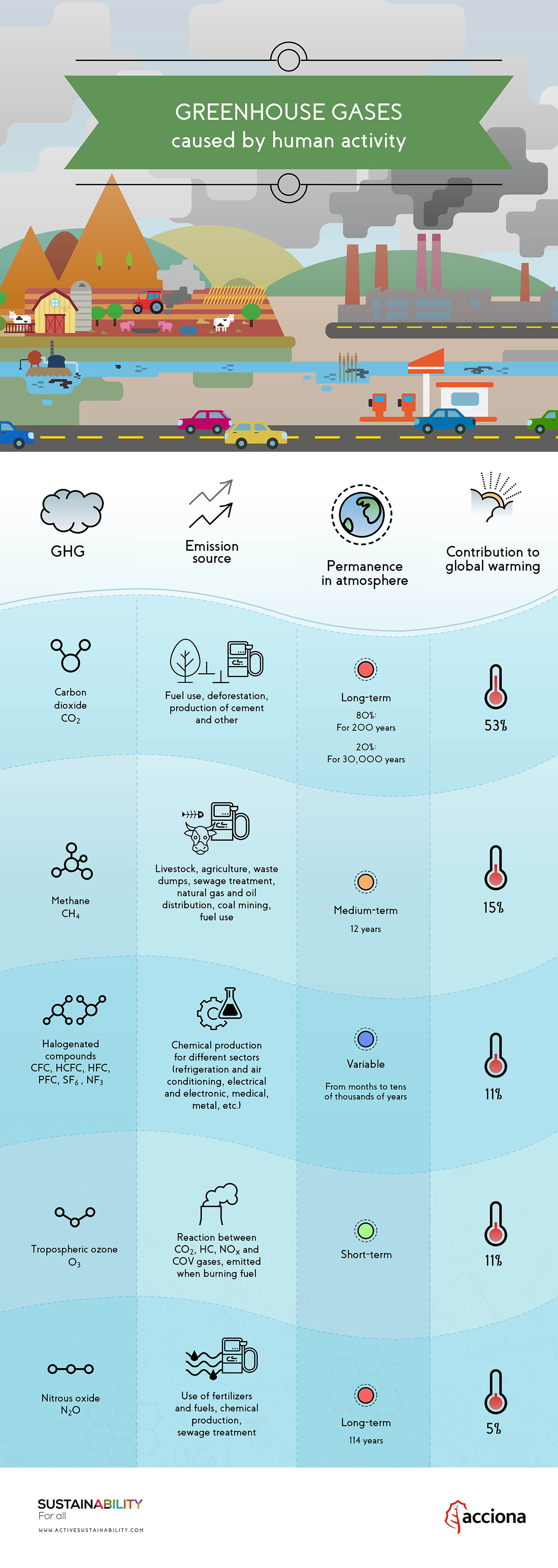
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
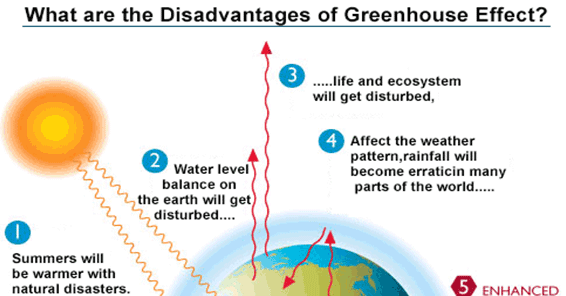
Disadvantages Of Greenhouse Effects Myassignmenthelp Com
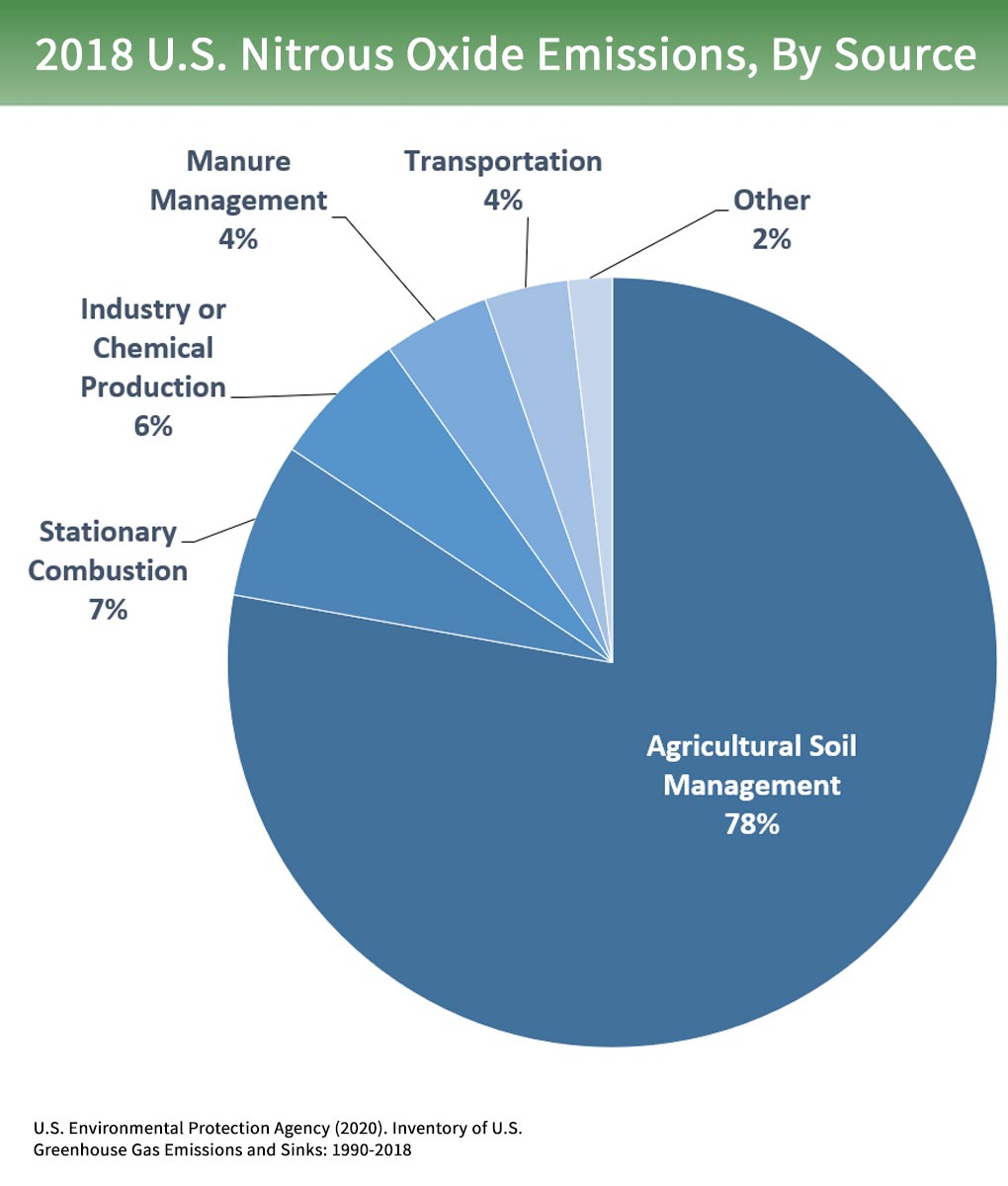
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
I would like to subscribe to Science X Newsletter.

Greenhouse gas definition chemistry. (To a lesser extent, surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap infrared radiation.). Water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and methane. They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60º F colder.
They are the cause of the greenhouse effect, a warming of the planet's surface. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets. Issue Volume 84, Issue 9.
We explore how this takes pl. Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) is a nontoxic, colorless, odorless gas. A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere.
Examples of Chemical Reactions in Everyday Life. Greenhouse gases only allow the Suns shoe wave radiation in, because of the chemical properties the gases do not interact with the sunlight. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3).
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs and emits infrared radiation. The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;. Some gases have a specialty that it can absorb infrared radiation emitted from the surface of the Earth.
The third worst greenhouse gas is methane. Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere. Combustion Definition in Chemistry.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases in the atmosphere that absorb and emit thermal radiation in a process known as the greenhouse effect—the mechanism by which solar radiation is captured and earth is warmed to an extent necessary for supporting life. Current Observations, Trends and Budgets 248 4.2.1 Non-CO 2 Kyoto Gases 248 4.2.1.1 Methane (CH 4) 248 4.2.1.2 Nitrous oxide (N 2O) 251 4.2.1.3. In doing so, it can maintain warmth on the earth’s atmosphere.
Only about 1 per cent is made up of natural greenhouse gases, but this comparatively small amount of gas makes a big difference. Polarity can be. Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun.
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by “greenhouse gases.” These heat-trapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. To estimate indirect greenhouse gas emissions from electricity use, please use Power Profiler or use eGRID subregion annual output emission rates as a default emission factor.
Greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect. 4.1.1 Sources of Greenhouse Gases 243 4.1.2 Atmospheric Chemistry and Feedbacks 245 4.1.3 Trace Gas Budgets and Trends 246 4.1.4 Atmospheric Lifetimes and Time-Scales 247 4.2 Trace Gases:. A gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2.
The major components of atmospheric gas—nitrogen, oxygen, and argon—are transparent to infrared radiation. Chemistry for the greenhouse Ultimately, Mirica’s goal is a recycling carbon chemistry that requires so little energy that it can run off sunlight. Gases in the Atmosphere.
The Industrial Revolution brought new industrial processes, an increase in the burning of fossil fuels, more extensive agriculture, and a rapid increase in the world's population. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. Learn greenhouse effect chemistry with free interactive flashcards.
The main greenhouse gases present in the earth’s atmosphere are methane, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Professor M Mercedes Maroto-Valer and Dr Curtis M. Absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details.
Individual subregion non-baseload emissions rates are also available on the eGRID Web site. Greenhouse gases are not a bad thing in. Then the definition of a dipole moment is a charge imbalance of electrons, and is represented by a vector (the lines with and arrow on one end).
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared radiation ( IR) and radiates heat in all directions. Indirect radiative forcing occurs when chemical transformations of the original gas produce a gas or gases that are greenhouse gases, when a gas influences the. Greenhouse Gases Atmosphere Definition When certain gases that have the ability to trap heat in the atmosphere are present in abundance, they cause greenhouse effect in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions. They do absorb the long wave radiation from the earth emit it back in the atmosphere do without greenhouse gases we would not g a anything living on the earth. The intensity of the downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – will depend on the atmosphere's temperature and on the amount of.
ACS Climate Science Toolkit | Greenhouse Gases Temperature is a measure of the average energy of molecular motion in a sample of matter:. Gases in the atmosphere can contribute to the greenhouse effect both directly and indirectly. Fossil fuel combustion converts carbon that had been stored deep in the Earth to carbon dioxide that enters the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. To and fro translation, intramolecular vibration (and lattice vibration in solids), and rotation (both entire molecules and intramolecular portions). This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases.This is called the "greenhouse effect".Most greenhouse gases are natural - water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth.
This leads to an increase in global temperatures, eventually resulting in a Greenhouse Earth. Methane comes from both natural and man-made sources. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
Atmospheric concentrations of several important greenhouse gases have increased significantly since large-scale industrialization began around 0 years ago4. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. These gases are called as greenhouse gases.
1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time. Find my revision workbooks here:. Greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist. Greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide (N2O) and other gases. This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases turn like a blanket, gripping Infra-Red radiation and. The primary greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Greenhouse gas Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surface.
It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun. Greenhouse gas emissions from homes and businesses vary from year to year often correlated with seasonal fluctuations in energy use caused primarily by weather conditions. The definition of a dipole is a pair of equal and oppositely charged poles separated by a distance.
The atmospheric gases and a greenhouse work in quite different ways, but the resulting effect, higher temperature in both cases, has led to the nomenclature “greenhouse gases” for the atmospheric gases responsible for the atmospheric warming effect. Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat in our atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
It is released by swamps and termites. Humans release methane trapped underground as a fuel, plus cattle ranching contributes to atmospheric methane. Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere.
A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space. The two major greenhouse gases both occur naturally and can be increased due to human activity.
Definition of greenhouse gas. Other greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide. Methane contributes to ozone depletion, plus acts as a greenhouse gas.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. Any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation. (IUPAC) International Congress of Crop Protection Chemistry.
This chemistry lesson teaches students about. Greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth. Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such.
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides. This calculation does not include any greenhouse gases other than CO 2.;. Greenhouse gases are defined and their effects are examined in this educational lesson.
In the CO 2 example we can see that the oxygen atoms are separated by distance. An atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by short-wave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longer-wavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;. Issue Volume 69, Issue 10.
Common Chemicals and Where to Find Them. The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. Noble Gases Properties, Uses and Sources.
How to Make a Homemade Volcano That Smokes. Your email address is used only to let the recipient know. “If we’re going to keep using these carbon-containing fuels that make CO2, we should be trying to make combustion carbon-neutral by using catalysts and the sun’s energy to convert CO2 back.
It also occurs naturally as it flows in a cycle between oceans, soil, plants and animals. Choose from 500 different sets of greenhouse effect chemistry flashcards on Quizlet. Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century.
Carbon dioxide (CO 2):. The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. A common greenhouse gas could be repurposed in an efficient and environmentally friendly way with an electrolyzer that uses renewable electricity to produce pure liquid fuels.
Direct effects occur when the gas itself is a greenhouse gas. Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, warming it. The large reservoir of carbon dioxide now present in our atmosphere, alongside other gases including water vapour, contributes to the greenhouse effect.
Although this nomenclature is misleading, it is in such common use that we use it here as well. Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect. 10 Worst Greenhouse Gases.
Is sulfur a greenhouse gas?. The main greenhouse gases. Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed with concern.
The most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are:. Definition & Examples :. A gas that causes the….
Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone, and methane;. Responsible for 63 percent of global warming over time, and 91 percent in the last 5 years, this gas is produced from burning fossil fuels, such as coal and oil.
Https://www.freesciencelessons.co.uk/workbooks In this video, we look at the Greenhouse Effect. The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere. Why do greenhouse gas levels matter?.
Greenhouse gases reflect heat radiation that the Earth emits, and stop it from being lost into space. Total residential and commercial greenhouse gas emissions, including direct and indirect emissions, in 18 have increased by 9.0 percent since 1990.

Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability

Glossary Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
6 B Increased Ghg Concentrations In Atmosphere Will Remain High For Centuries And Affect Future Climate Noaa Climate Gov
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
Environment For Kids Global Warming

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Edexcel As Unit 2 Green Chemistry Notes

Q Tbn 3aand9gctqwv6hr0l443owvtpvrz3yj0vkuiyytqvpbw Usqp Cau

Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Presented By Mamoona Ghaffar Docsity
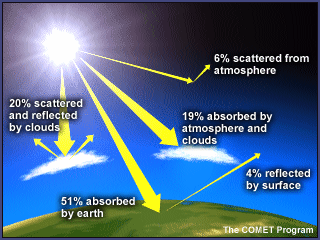
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
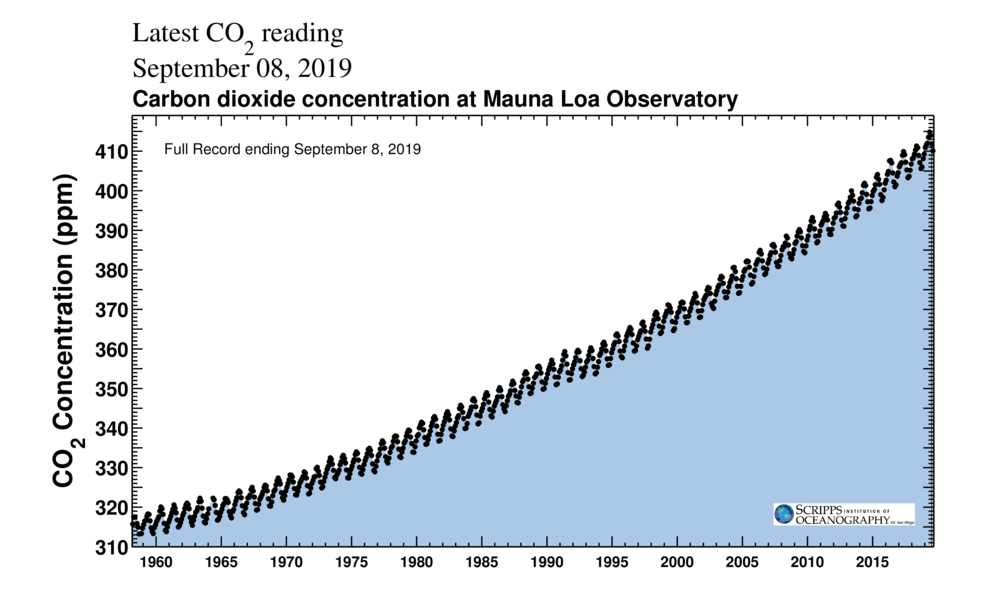
Climate Explained Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate

Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium

Ghgs And Gwp

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
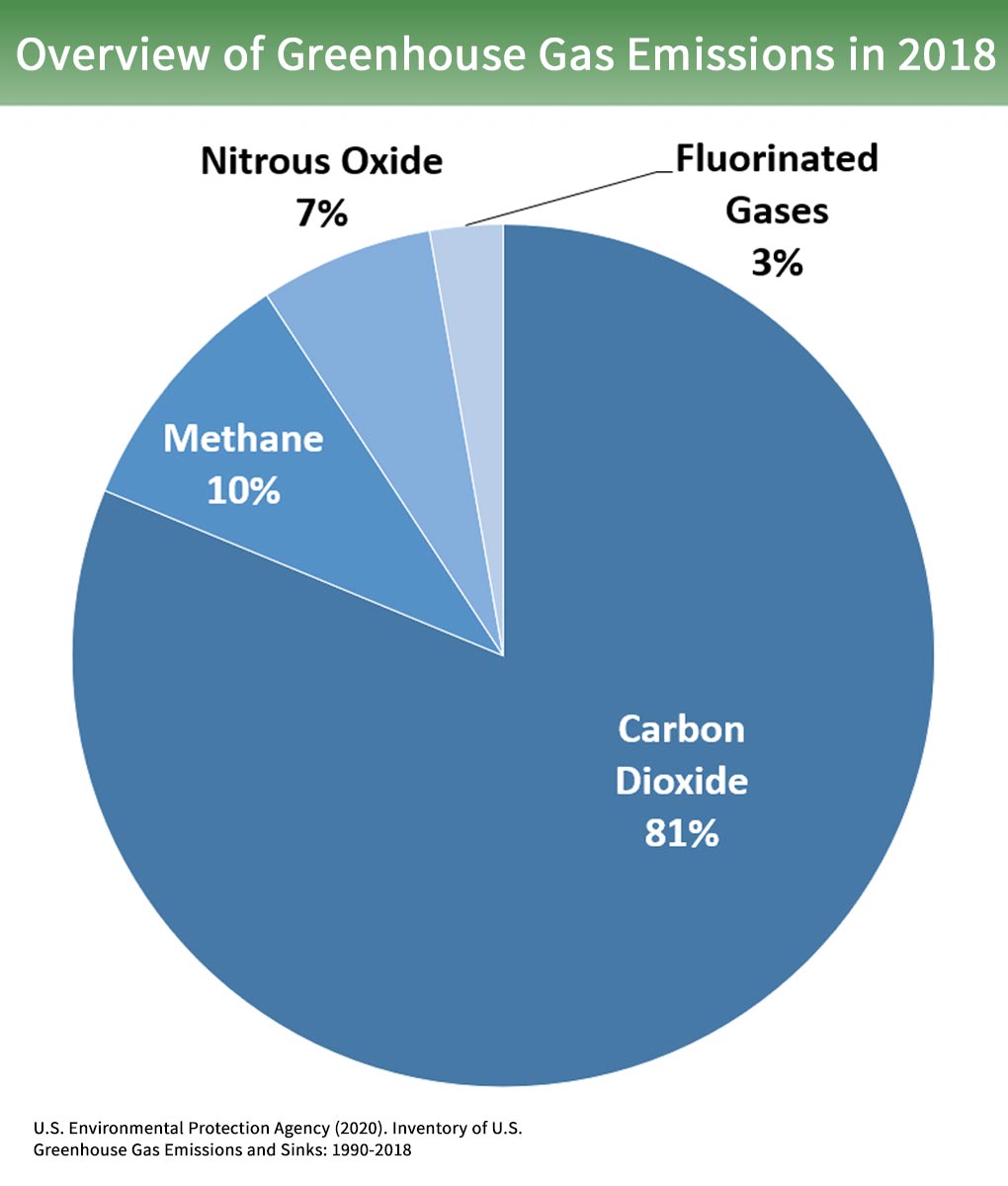
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Team Braunschweig Project Content 14 Igem Org

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends European Environment Agency

The Greenhouse Effect Introduction To Chemistry

Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
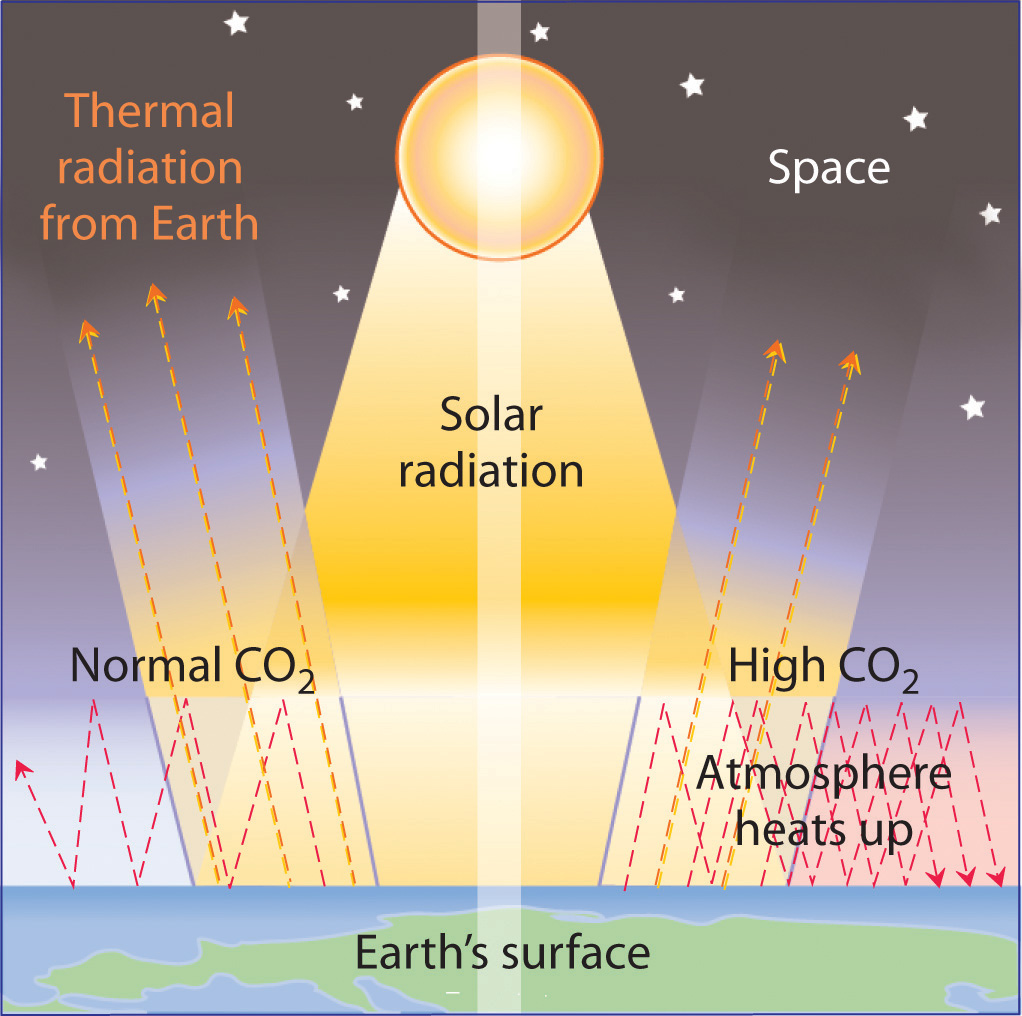
Energy Sources And The Environment

Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From

Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
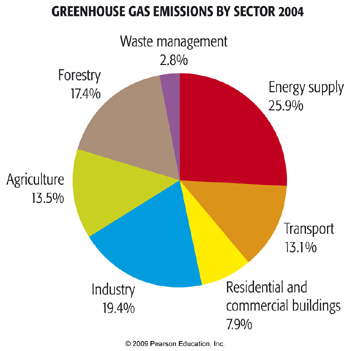
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming

Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview

Difference Between Methane And Ethane Definition Chemical And Physical Properties
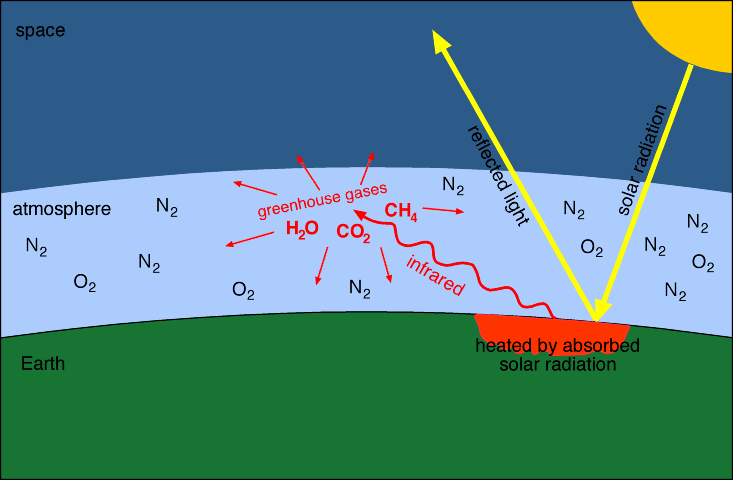
The Greenhouse Effect
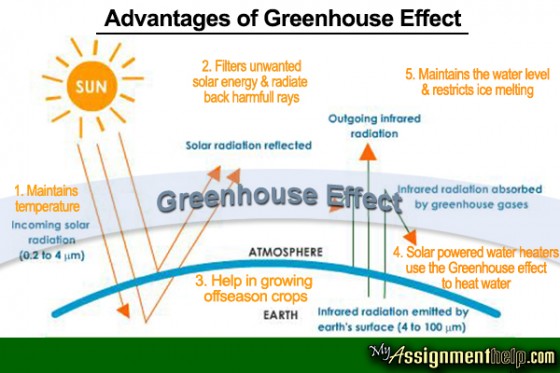
The Greenhouse Effect Know The Advantages And Disadvantages

Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Using Models To Make Predictions National Geographic Society
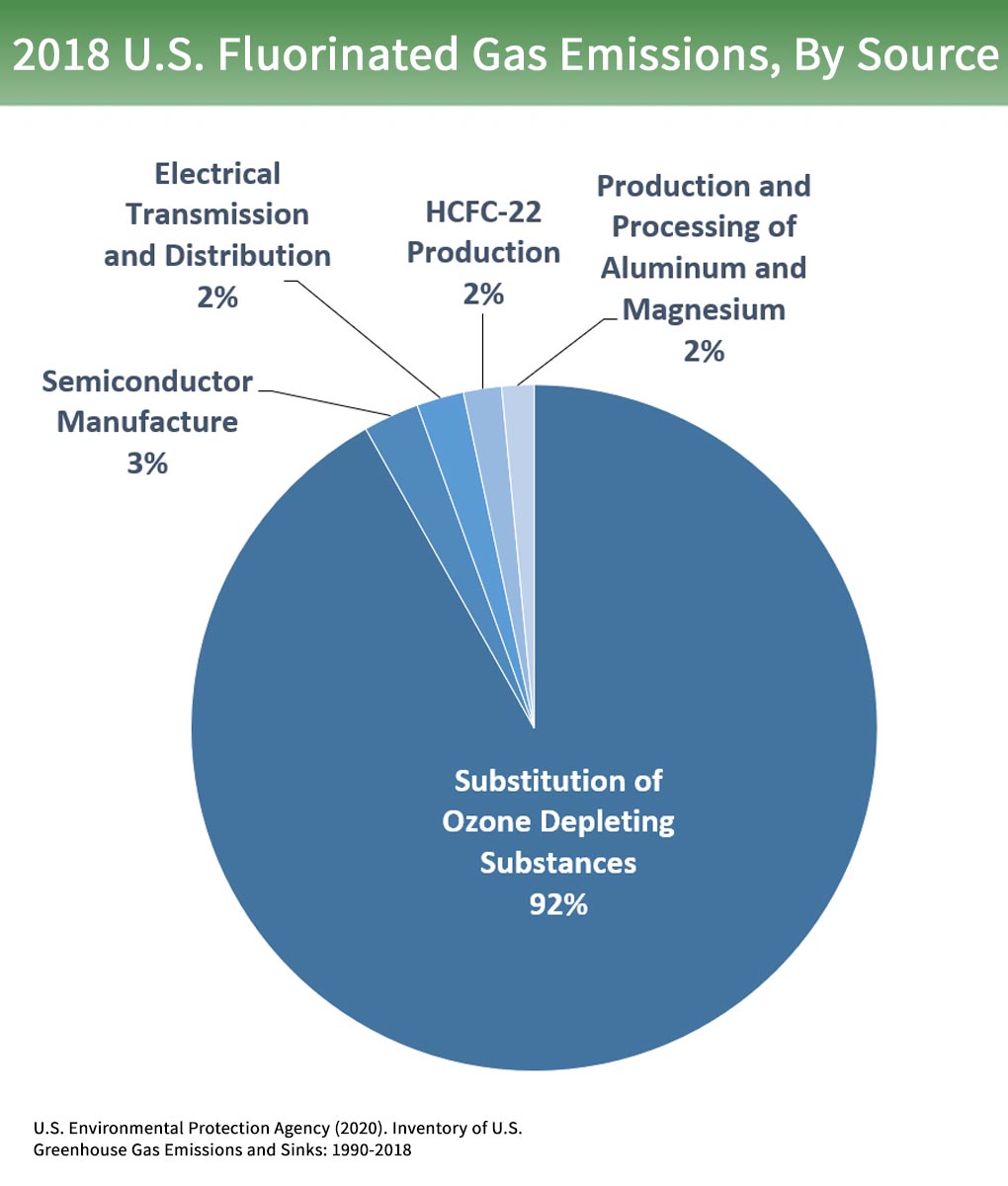
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
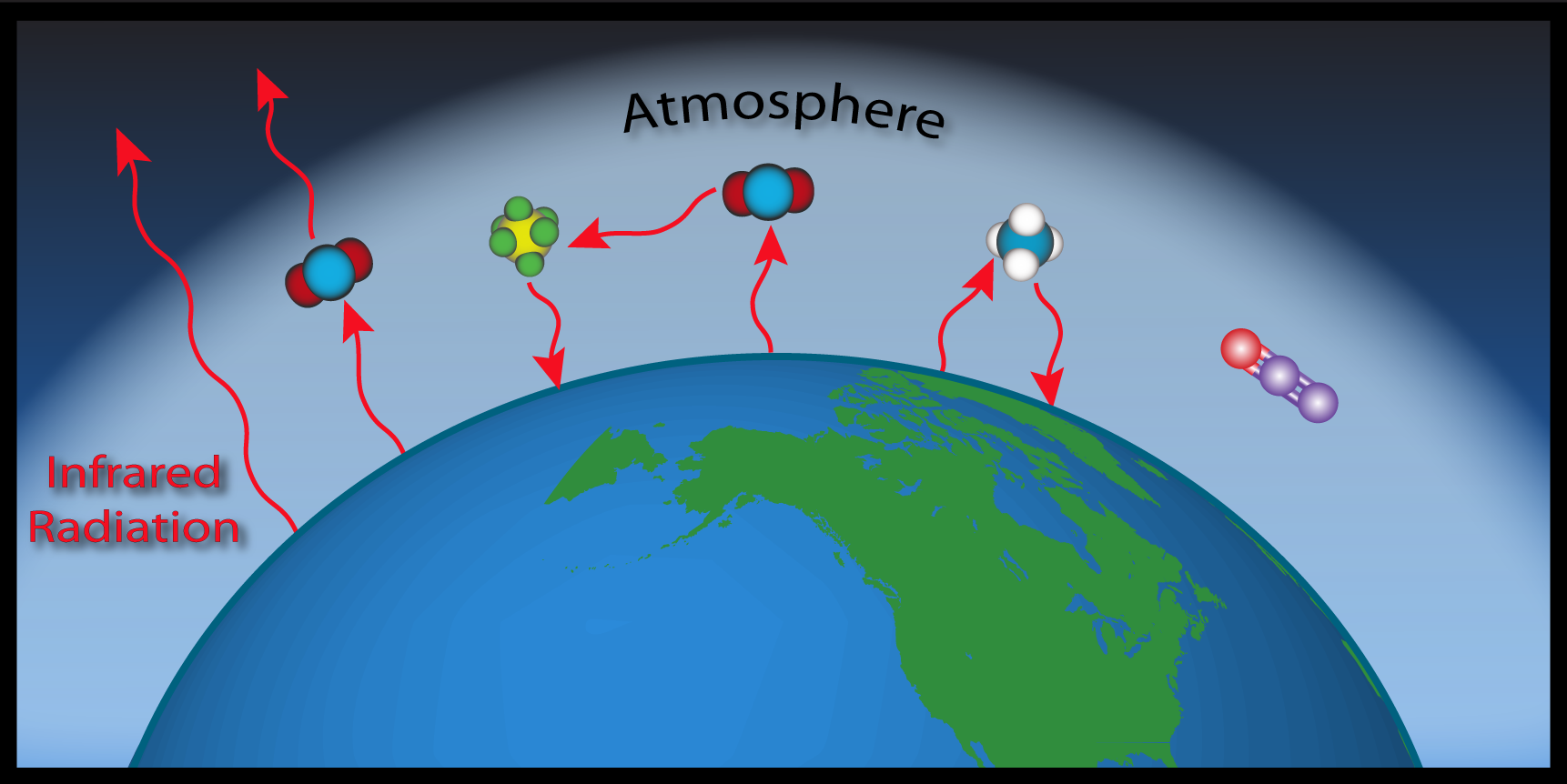
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

Methane Is Like Co2 On Steroids When It Comes To Trapping Heat

Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay
1
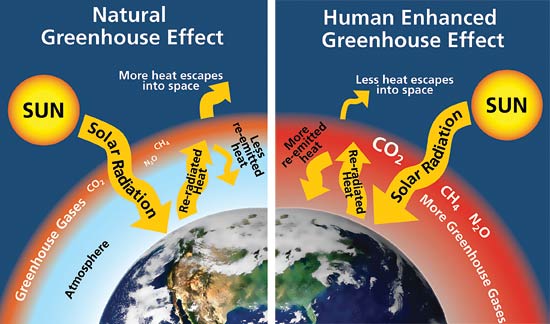
Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
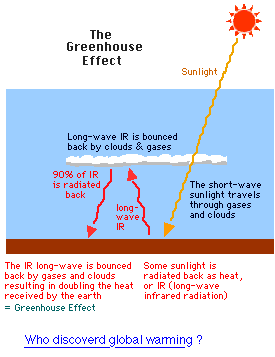
Introduction

Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming
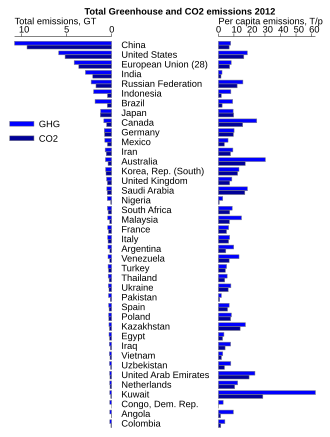
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
Q Tbn 3aand9gcswtw6jmpki0thvbw9s03clyicmq0e Etfhbtsrvhxuoxvo5xud Usqp Cau

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrkshs4yxsmfkaj 7o4ctqd2sjucsgee2fpvlscwmrhqroqc Usqp Cau

Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society

Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg

Greenhouse Gases Ghgs Greenhouse Gas Greenhouse Effect
1

Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change

Green Chemistry What Is It Encourages Environmentally Conscious Behaviour Reduces And Prevents Pollution Reduces The Destruction Of The Planet Ppt Download
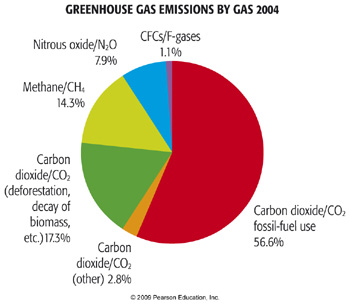
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming
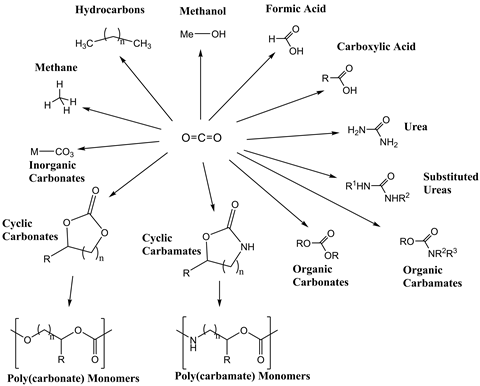
Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Gas Or Useful Chemical Feedstock Sponsored Chemistry World

Global Warming

Difference Between Methane And Fluorinated Gases Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Greenhouse Effect Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate

The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus

Pdf The Greenhouse Effect And Its Impacts On Environment

Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
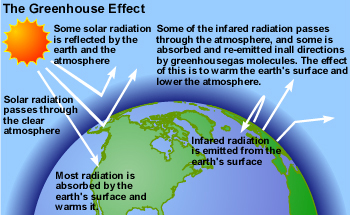
Greenhouse Effect North Carolina Climate Office

Atmosphere Webquest

Edexcel As Unit 2 Green Chemistry Notes Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas

Greenhouse Effect Dictionary Definition Greenhouse Effect Defined
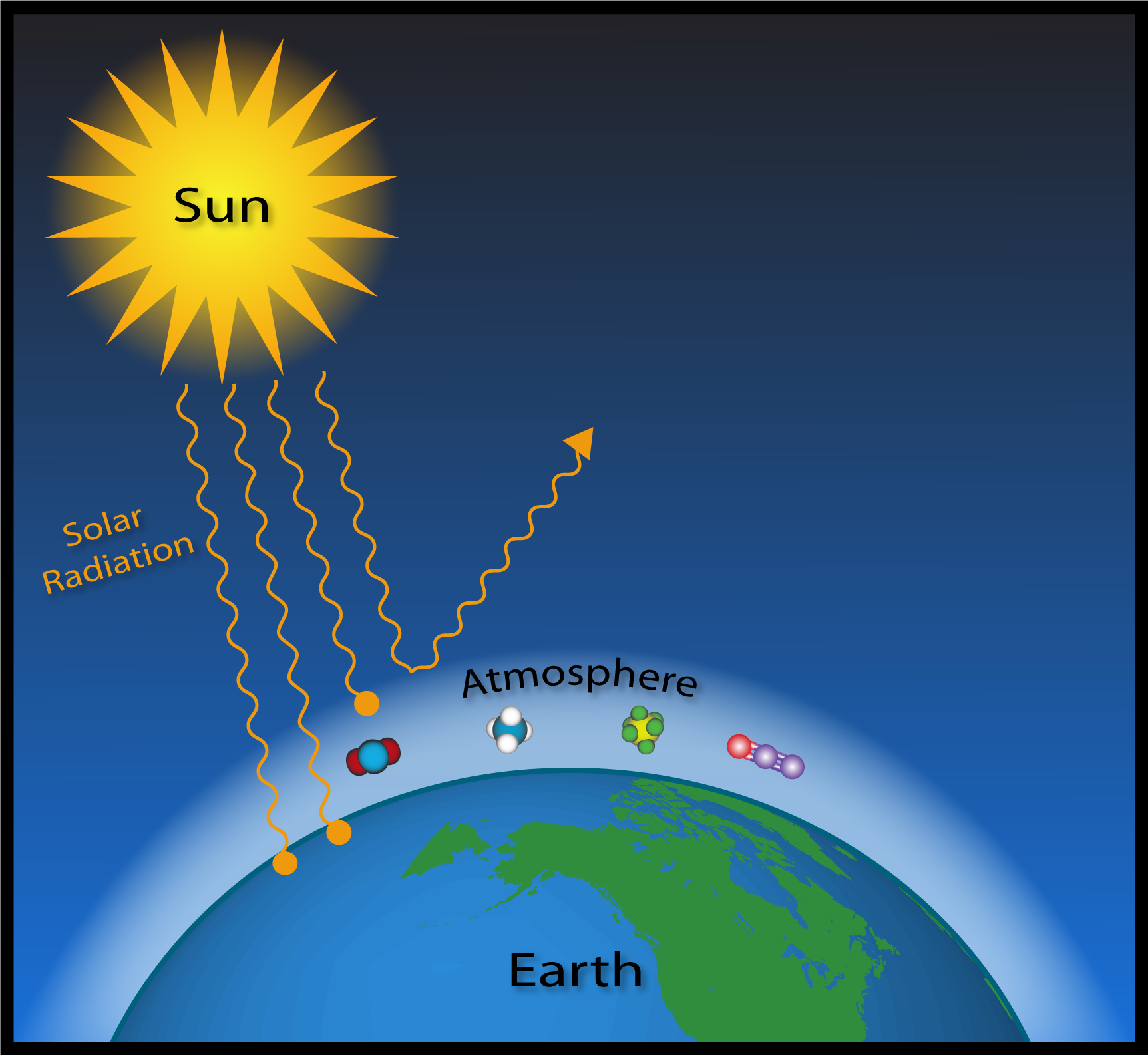
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
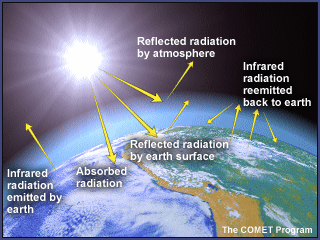
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases

Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society

5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
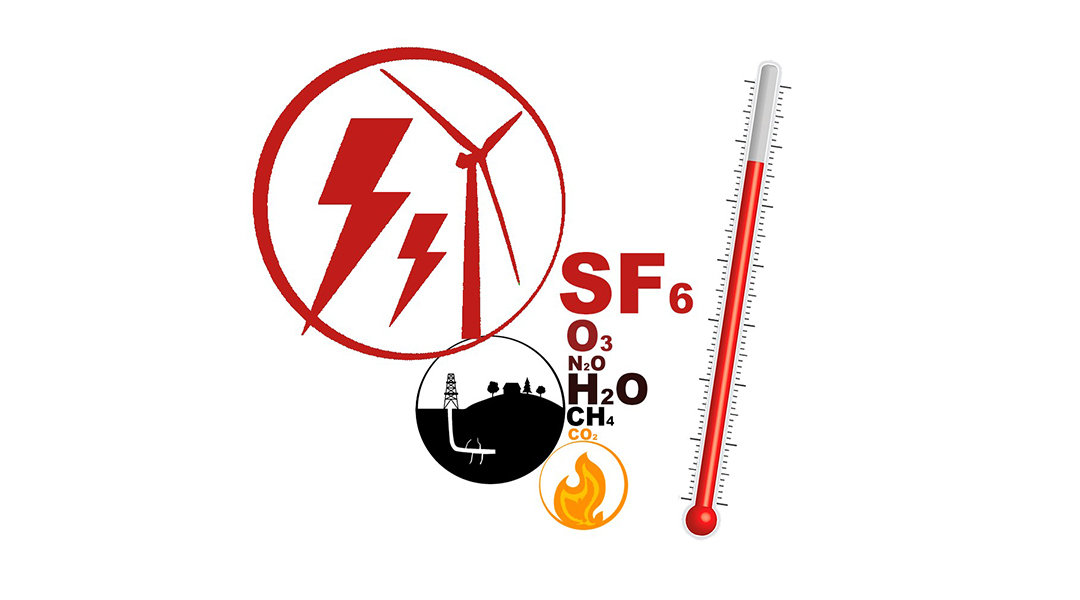
Sf6 Worries The Most Potent And Persistent Greenhouse Gas Advanced Science News
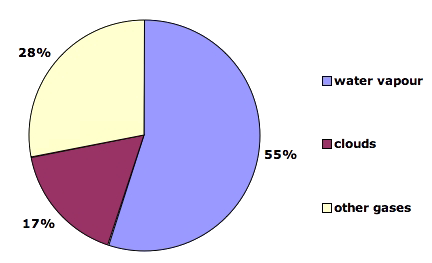
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici

Greenhouse Effect Hindi Vimal Singh Rathore Youtube

Untitled Document

Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions Internationale Klimaschutzinitiative Iki

Q Tbn 3aand9gcrz1uacukqwbnjfjiy8eq6rnbuoqvk2 Zqwxq Usqp Cau

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
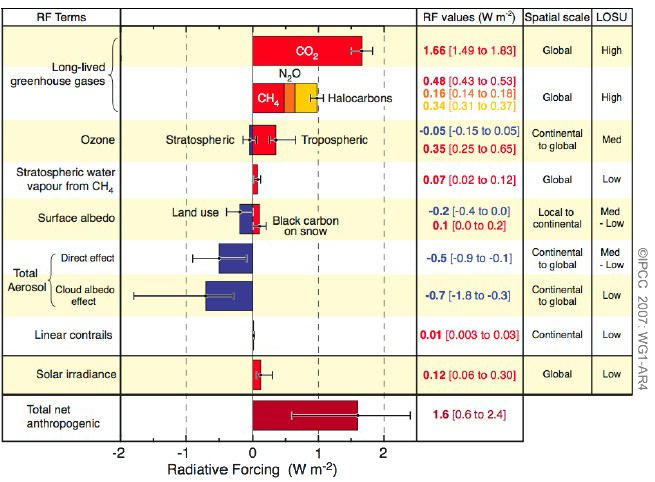
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
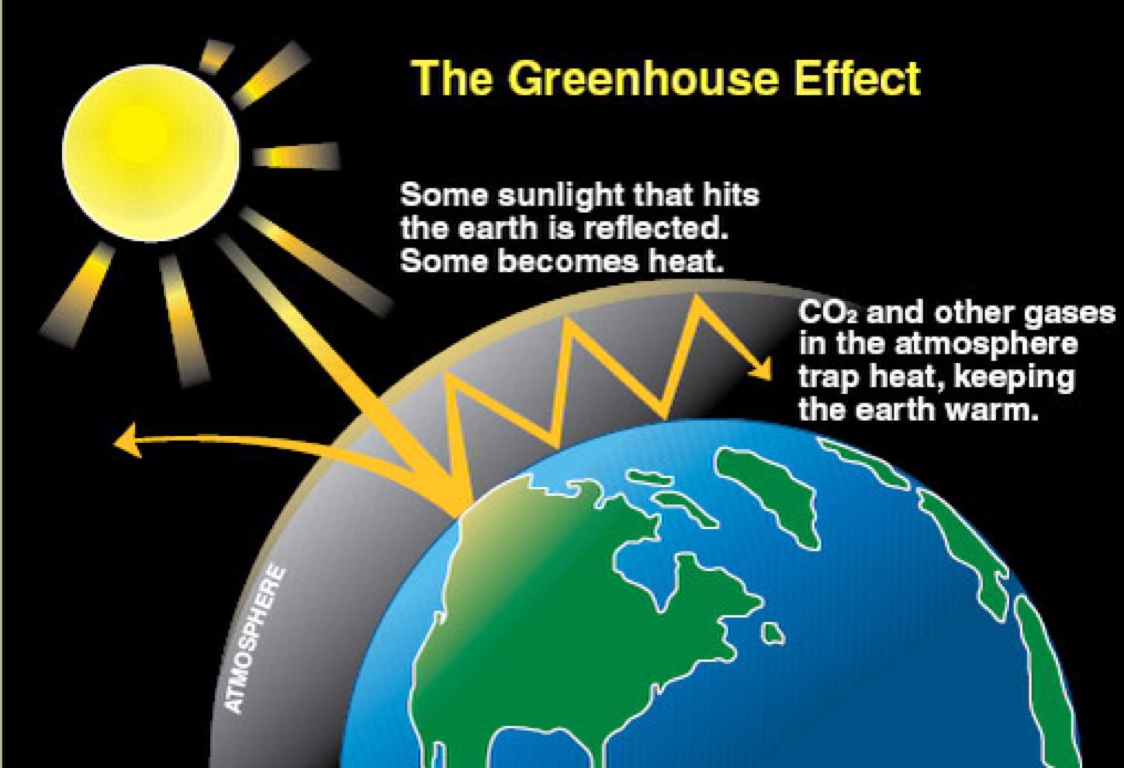
What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic
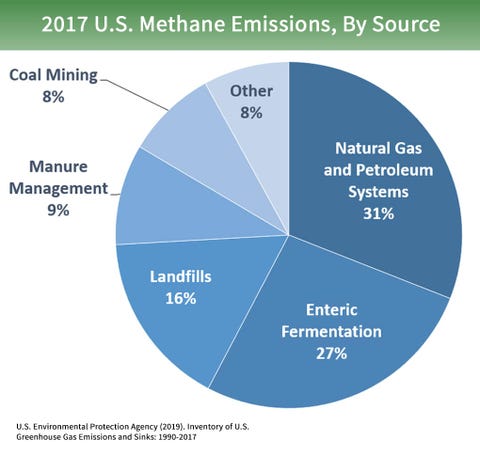
What Is Methane Methane Greenhouse Gas Facts
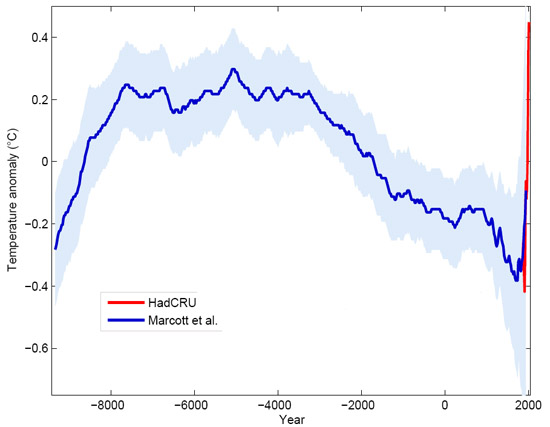
The Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Effect

Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects

Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science
Greenhouse Gas Reduction

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



