Greenhouse Gas Emissions Definition
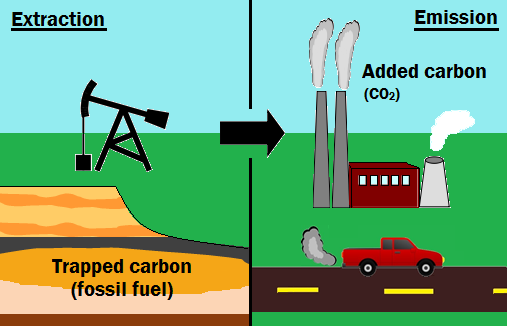
Anthropogenic Carbon Emissions Energy Education

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Canada Ca

Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire

The Future Of Oil And Gas Is Now How Companies Can Decarbonize Mckinsey
Greenhouse Gas Reduction

Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gas emissions definition. The emission into the earth's atmosphere of any of various gases, esp carbon dioxide, that contribute to the greenhouse effect. Based on these points, we propose the following definition for a net zero company:. This heat trapping phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun. Greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it. How to Reduce Your Greenhouse Gas Emissions.
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions. It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun. Greenhouse gases are those that absorb and emit infrared radiation in the wavelength range emitted by Earth.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Net zero means that the UK’s total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions would be equal to or less than the emissions the UK removed from the environment 1.This can be achieved by a combination of emission reduction and emission removal. Net zero can be achieved by emission reduction and removal.
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases that increase the temperature of the Earth due to their absorption of infrared radiation. They pledged that, by 25, they will have cut greenhouse gas emissions by at least 26% below 05 levels. A gas that causes the….
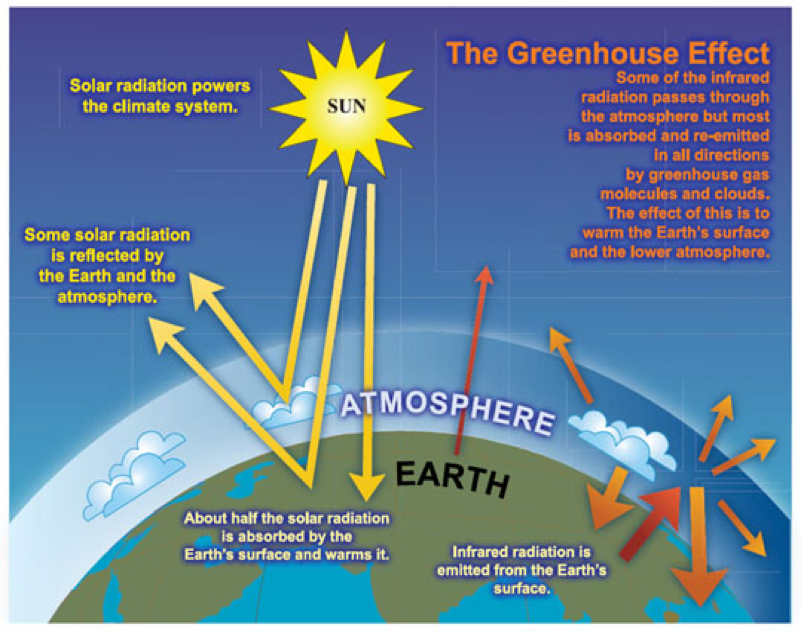
Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion. Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere. The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth.
ENERGY STAR® is the government-backed symbol for energy efficiency, providing simple, credible, and unbiased information that consumers and businesses rely on to make well-informed decisions.Thousands of industrial, commercial, utility, state, and local organizations—including about 40% of the Fortune 500®—partner with the U.S. Learn more about GHGs ». FILE - In this Aug.
Greenhouse gas emissions in British English. CH4 is more potent than CO2 because the radiative forcing produced per molecule is greater. The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere.
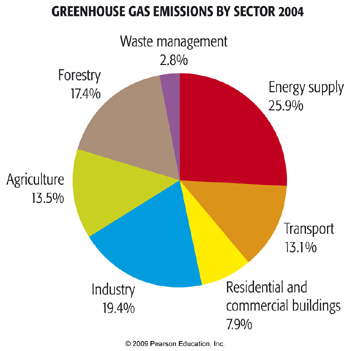
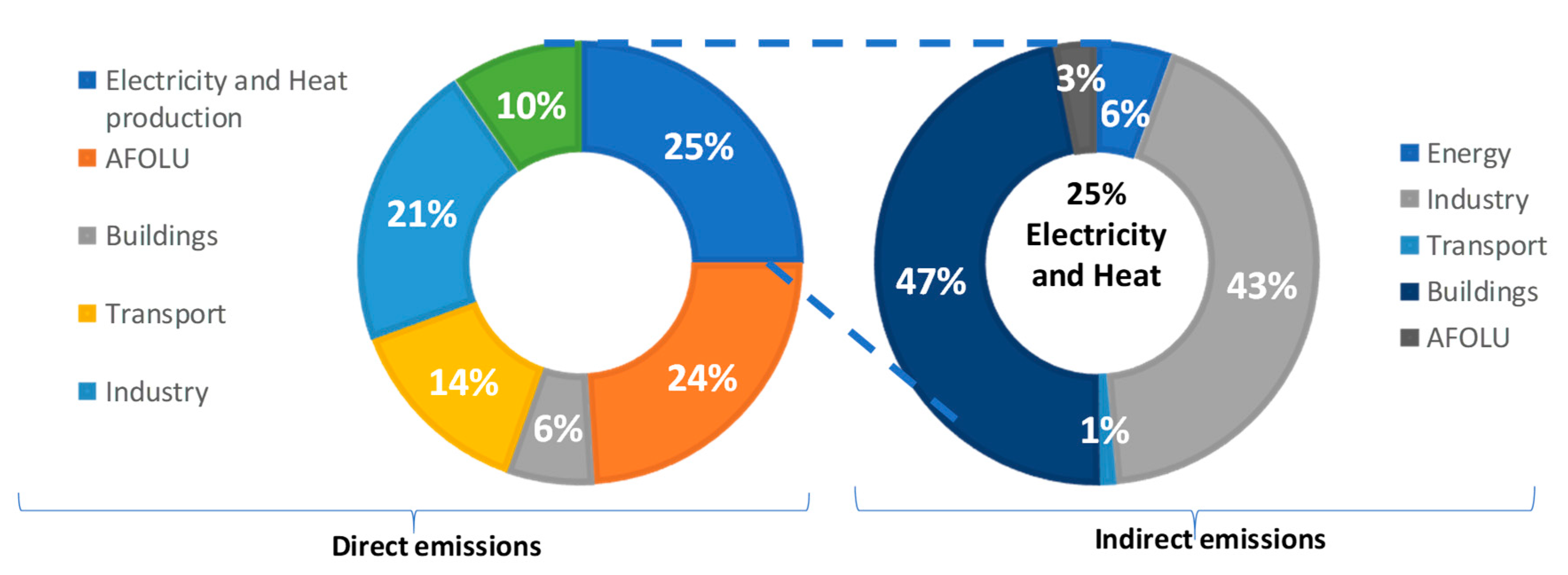
The largest economic sector in greenhouse gas emissions was the transportation sector, representing 29 percent of all emissions. Greenhouse gas emissions accounting is measuring the amount of greenhouse gases (GHG) emitted during a given period of time by a polity, usually a country but sometimes a region or city. When we burn fossil fuels like coal and petroleum gas, carbon dioxide and other gases are released into the atmosphere.
Production-based (also known as territorial-based) and consumption-based. Explore the data through our map app, FLIGHT ». Greenhouse emission - a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation greenhouse gas CFC, chlorofluorocarbon - a.
Given current concentrations and ongoing emissions of greenhouse gases, it is likely that by the end of this century global mean temperature will continue to rise above the pre-industrial level. Its goal is to keep global warming from worsening another 2 C above pre-industrial levels. , 19 file photo, gamers play the latest video games from Electronic Arts at the Gamescom in Cologne, Germany.
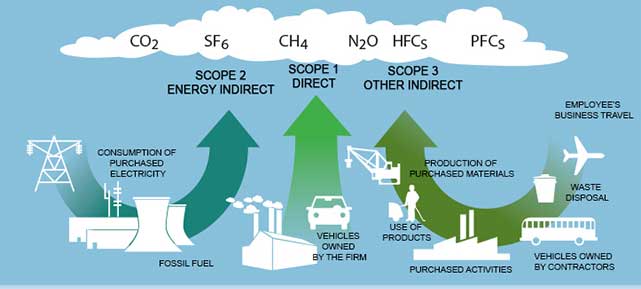
Scope 1 covers direct emissions from owned or controlled sources. The essential tenet of the Kyoto. A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared radiation (IR) and radiates heat in all directions.
Greenhouse gas inventories are a type of emission inventory that are developed for a variety of reasons. Policy makers use inventories to develop strategies and policies for emissions reductions and to track the progress of those policies. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect.
A net zero company will set and pursue an ambitious 1.5°C aligned science-based target for its full value-chain emissions. In the United States, most of the emissions of human-caused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gases (GHG) come primarily from burning fossil fuels—coal, hydrocarbon gas liquids, natural gas, and petroleum—for energy use.Economic growth (with short-term fluctuations in growth rate) and weather patterns that affect heating and cooling needs are the main factors that drive the amount of energy consumed. Define Greenhouse gas emissions report.
This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases.This is called the "greenhouse effect".Most greenhouse gases are natural - water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth. These are recorded in GHG emission inventories submitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and form the official data for international climate policies. See the Data Highlights ».
California’s greenhouse gas emissions have decreased even as California experienced population and economic growth:. Any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation. Greenhouse gas emissions are calculated based on the gallons of gasoline and diesel sales, relying upon standardized Energy Information Administration conversion rates for E10 fuel (gasoline with 10% ethanol) and standard diesel.
(To a lesser extent, surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap infrared radiation.). Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. A gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2.
Greenhouse gas Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. Scope 2 GHG emissions are indirect emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the Agency.
Scope 2 includes emissions that result from the generation of electricity, heat or steam purchased by the Agency from a utility provider. Many experts consider that the tipping point. Carbon emissions reporting is a form of reporting for the emissions created from commercial activity, usually as a strategy for identifying contributions to Global warming and to influence subsequent policies to mitigate human caused climate change.Reporting usually captures outputs from processes like burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, agricultural practices (e.g., the use of fertilizer.
Any remaining hard-to-decarbonise emissions can be compensated using certified greenhouse gas removal. 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time. A building with a roof and sides made of glass, used for growing plants that need warmth and….
Carbon dioxide (0.04%), nitrous oxide, methane and ozone are trace gases that account for almost one tenth of 1% of Earth's atmosphere and have an appreciable greenhouse effect. Human emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world’s most pressing challenges. This article is about emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG emissions) classified by technical processes.
During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. These gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to produce electricity. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to deliver cost-saving. Concentration, or abundance, is the amount of a particular gas in the air. Examples of how to use “greenhouse gas emissions” in a sentence from the Cambridge Dictionary Labs.
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gas Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surface.
By increasing the heat in the. Greenhouse gas emissions are categorised into three groups or 'Scopes' by the most widely-used international accounting tool, the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol. Responsible for 63 percent of global warming over time, and 91 percent in the last 5 years, this gas is produced from burning fossil fuels, such as coal and oil.
Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat just like the glass roof of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gas - Greenhouse gas - Methane:. The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it.
Streaming high-definition video and games can result in significant greenhouse gas emissions, depending on the technology used, according to a German government-backed study released Thursday. Scientists use inventories of natural and anthropogenic (human-caused) emissions as tools when developing atmospheric models. Such measures are used to conduct climate science and climate policy.
Greenhouse emission synonyms, greenhouse emission pronunciation, greenhouse emission translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse emission. Explore GHG emissions from the largest sources and sectors:. Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century.
These emissions trap heat close to the earth, causing what is known as the. Emissions from the transportation sector totaled 1.86 billion metric tons, up 0.5 percent from 16 and the highest level in nine years. Other greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide.
Greenhouse gas n any gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect green′house gas` n. Although some emissions are natural, the rate of which they are being produced has increased because of humans. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane.
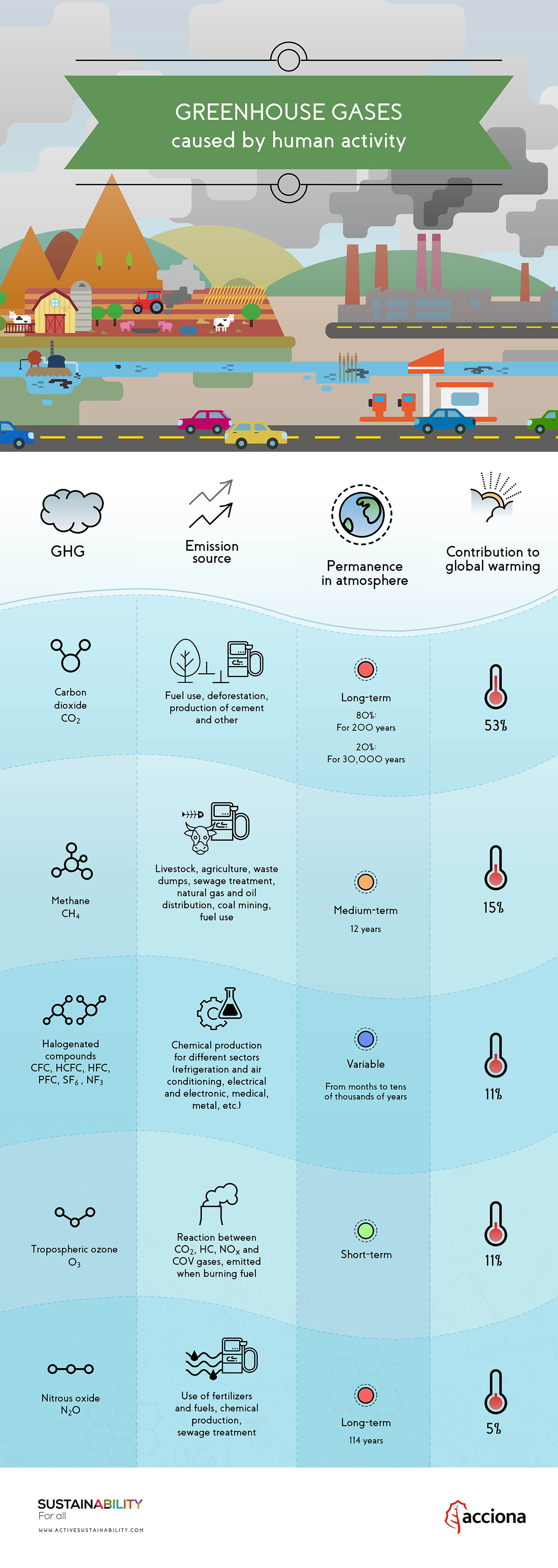
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) makes up the vast majority of greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, but smaller amounts of methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) are also emitted. Methane (CH4) is the second most important greenhouse gas. Beyond that, the consequences of climate change become unstoppable.
In addition, the infrared window is less saturated in the range of wavelengths of radiation absorbed by CH4, so more molecules may fill in the region. The United States produced 6.7 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 18, the second largest in the world after China and among the worst countries by greenhouse gas emissions per person.Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 10s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation, which. Larger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to higher concentrations in the atmosphere.
A gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2. Greenhouse gases reflect heat radiation that the Earth emits, and stop it from being lost into space. The main greenhouse gases.
Scope 2 covers indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating and cooling consumed by. 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth’s history. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases.
Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect. Any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons. It also occurs naturally as it flows in a cycle between oceans, soil, plants and animals.
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxide. GHGs are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. (ˈɡriːnˌhaʊs ɡæs ɪˈmɪʃənz) plural noun.
The principal GHGs, also known as heat trapping gases, are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and the fluorinated gases. Carbon dioxide (CO 2):. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60º F colder.
Or "report" means a note that uses available data to assess whether a legislative measure is likely to directly cause a net increase or decrease in greenhouse gas pollution within the ten-year period following its enactment, including identifying new sources of greenhouse gas emissions, any increase or decrease in emissions from existing sources, and any. 15 emissions were 10 percent lower than peak levels in 04, and 16 emissions dropped below 1990 levels for the first time.*. They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
In addition, Eurostat disseminates GHG emissions classified by emitting economic activities. The two major greenhouse gases both occur naturally and can be increased due to human activity. 2 To set the scene, let’s look at how the planet has warmed.
The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement that aimed to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and the presence of greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight. There are two main, conflicting ways of measuring GHG emissions:.

Vedanta Sustainable Development Report 18 19

Mitigation Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Malta Resources Authority

Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions Internationale Klimaschutzinitiative Iki

Global Protocol For Community Scale Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventories By Ghg Protocol Issuu
1
California Greenhouse Gas Inventory Shows State Is Tracking To Achieve Ab 32 Target Green Car Congress

Emissions Sources Climate Central

Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting

Greenhouse Gas Emissions
1

Edgar Edgar Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases European Commission
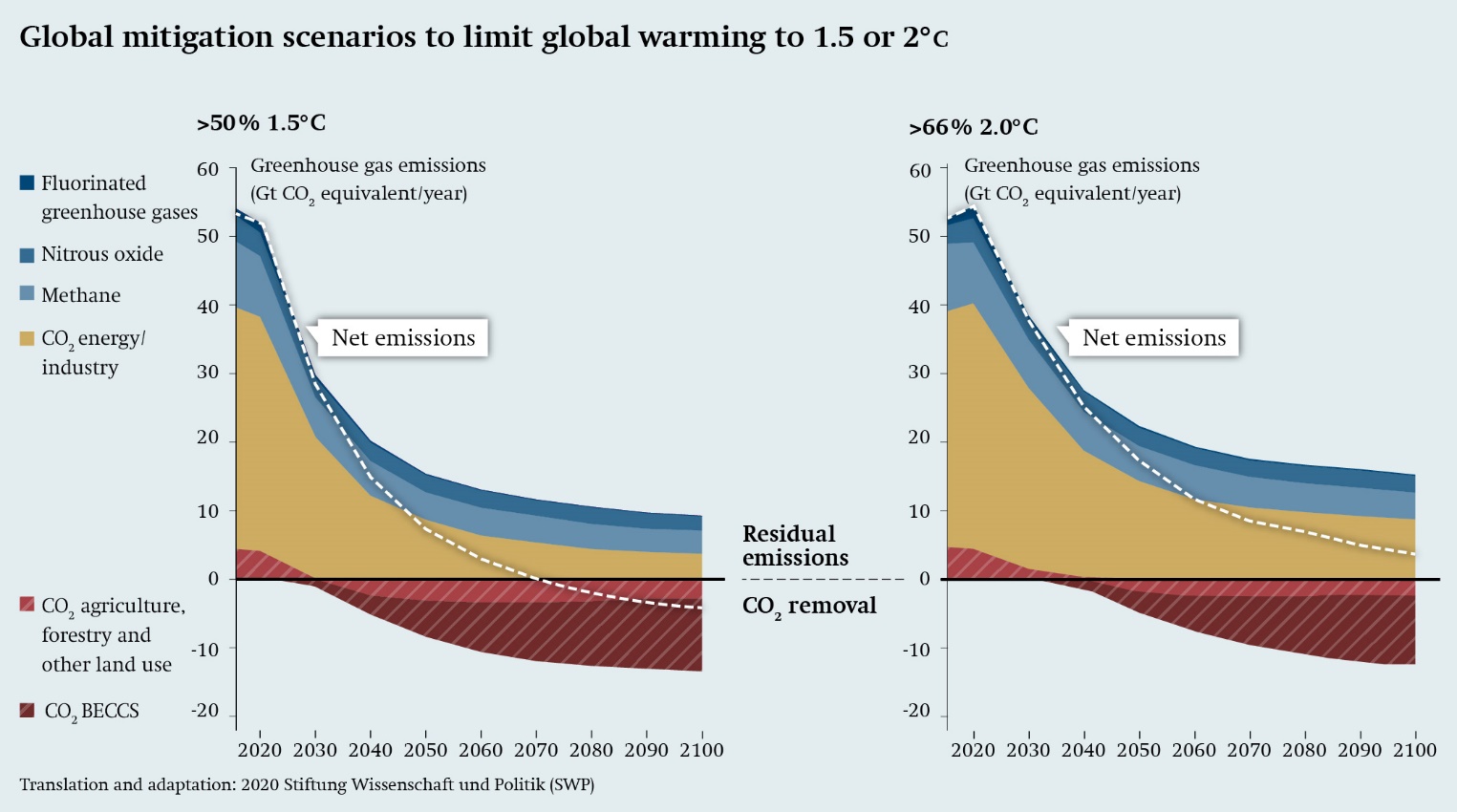
Unconventional Mitigation Swp
Reducing Emissions In Our Operations Sustainability Home
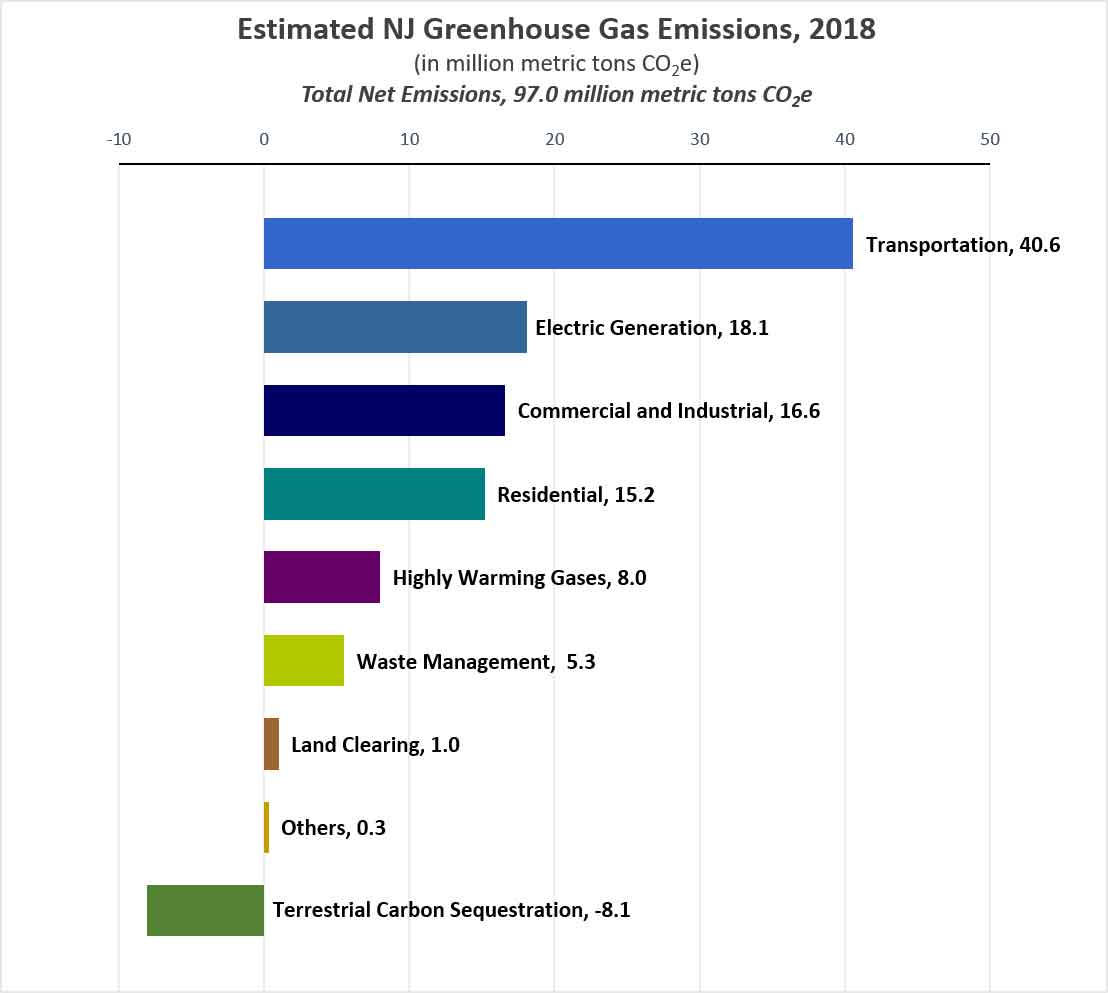
Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Archive Agriculture Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Statistics Explained

Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iberdrola
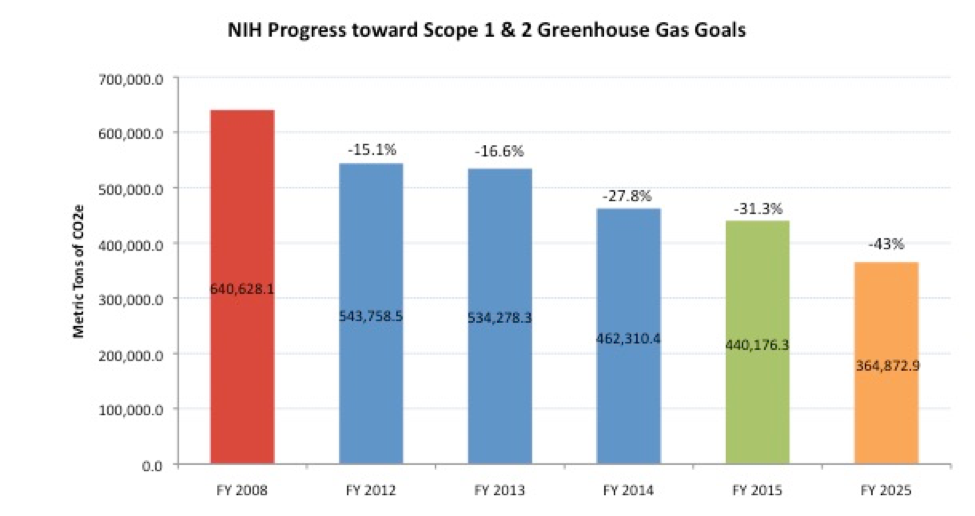
Greenhouse Gas Reduction

Greenhouse Gases Copernicus

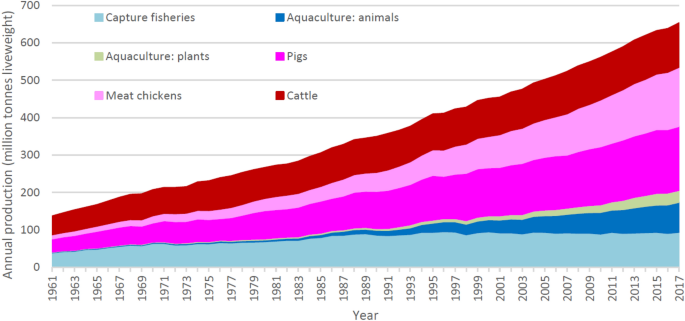
Impact Of Agriculture On Climate Change

Greenhouse Gas Emission An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Development Of Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions In Germany In Sectors Download Scientific Diagram

What Are Carbon Emissions And Why Do They Matter Earthhero Blog

The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef

Carbon Neutral Buildings Creating Value Through Architecture White Arkitekter

Iso 1 18 En Greenhouse Gases Part 1 Specification With Guidance At The Organization Level For Quantification And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Removals

Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Water Footprints Of Typical Dietary Patterns In India Sciencedirect
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrgjvklw5bbgs9gg Iiojsqdbfcprkgsaeplscilq2vlkotsalb Usqp Cau

Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa

Calameo National Strategy Low Carbon

Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire

Embodied Ghg Emissions Of Buildings The Hidden Challenge For Effective Climate Change Mitigation Sciencedirect

Samsung
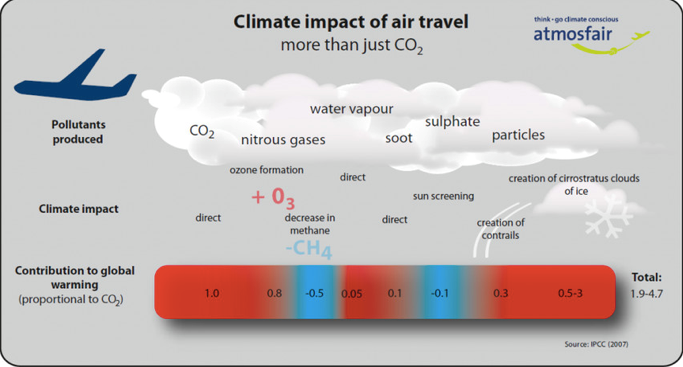
Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation White Papers Eesi
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
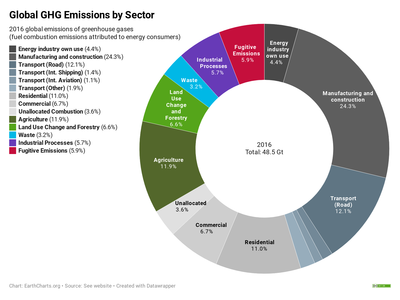
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
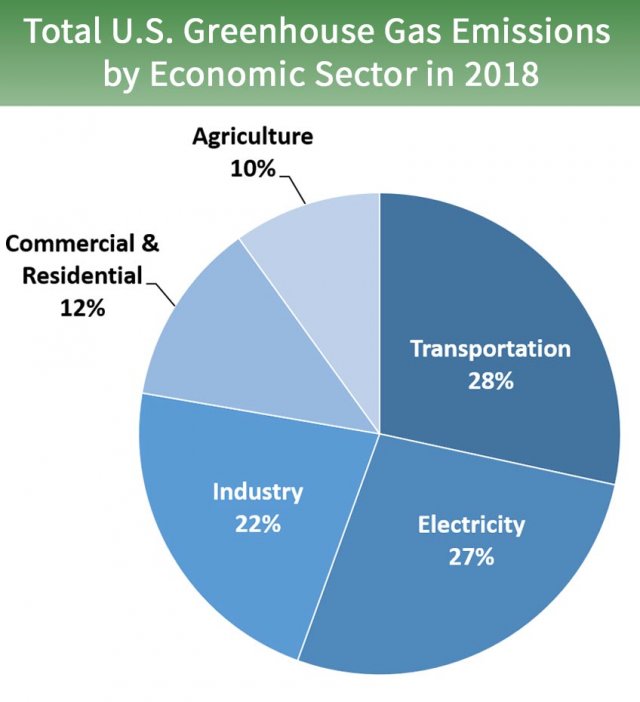
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Why Carbon Neutral And Carbon Zero Are Not The Same Daily Green World

Untitled Document
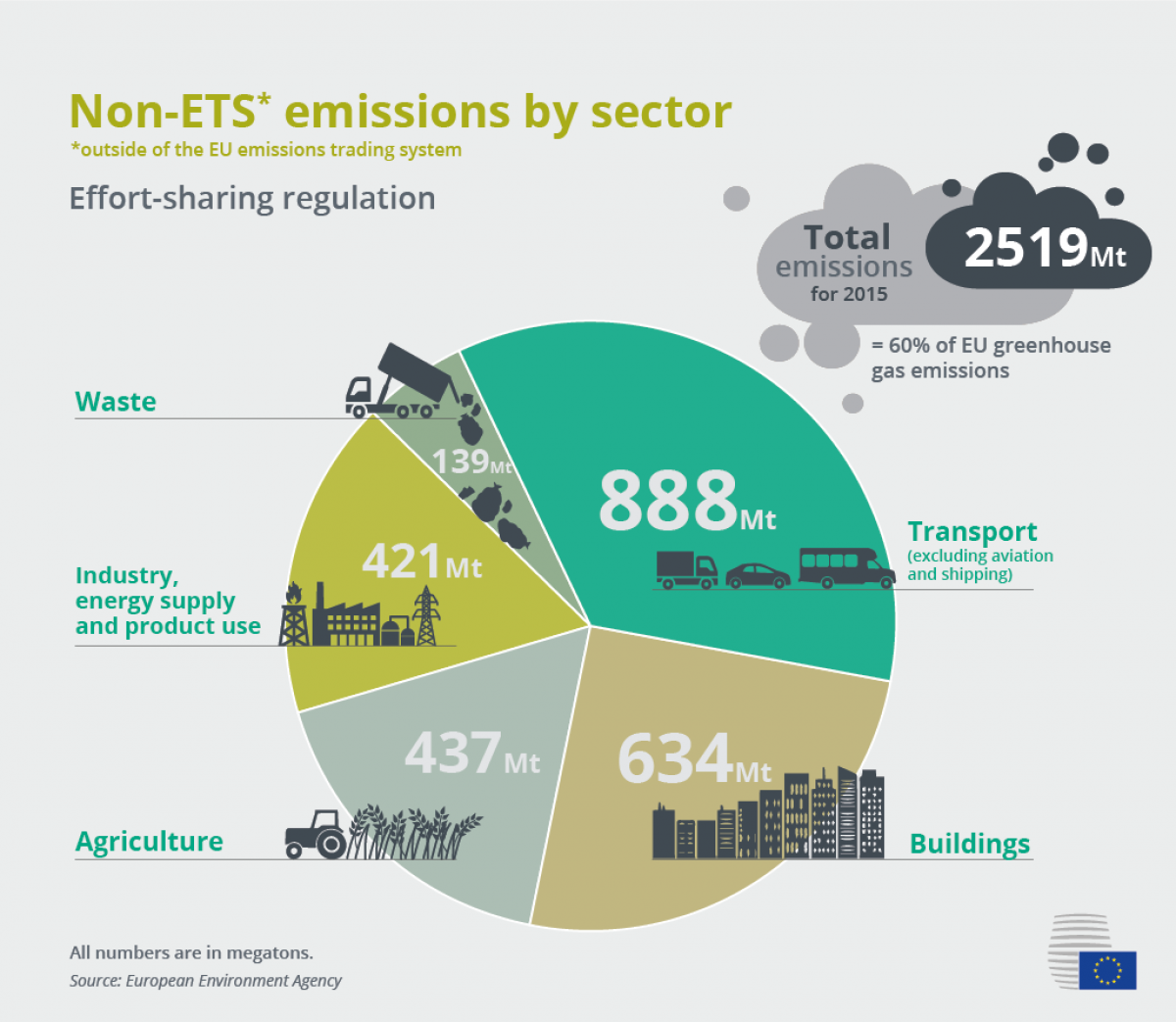
Germany S Climate Obligations Under The Eu Effort Sharing Scheme Clean Energy Wire
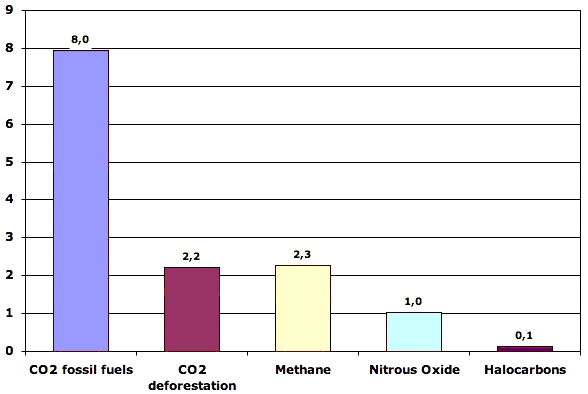
What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici

Greenhouse Gas Inventory

How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ghg Emissions Emissions

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
Net Zero And The Different Official Measures Of The Uk S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Office For National Statistics
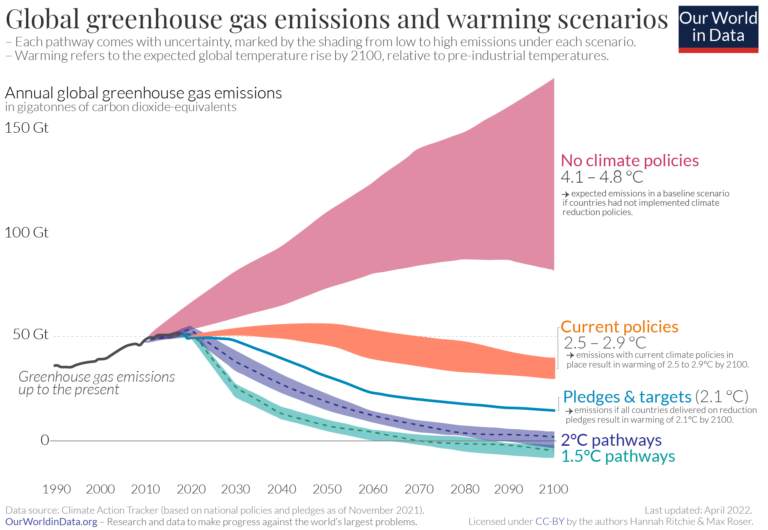
Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions

How Do You Calculate Scope 3 Emissions News Open Sourced Workplace

Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples
Emission Impossible Corporate Knights
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Carbon Dioxide Uptake By Cement Based Materials A Spanish Case Study Html
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Global Aquaculture Scientific Reports

Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change

Habitats Climate Change Cc1 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Biodiversity Fi

Ghg Emissions Environmental Reporting
Methane Emissions In The Oil And Gas Industry American Geosciences Institute

Iso 2 19 En Greenhouse Gases Part 2 Specification With Guidance At The Project Level For Quantification Monitoring And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions Or Removal Enhancements
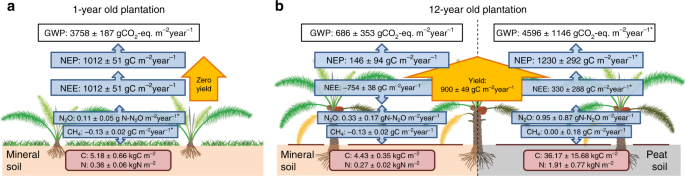
Measured Greenhouse Gas Budgets Challenge Emission Savings From Palm Oil Biodiesel Nature Communications
.png)
Fact Sheet The Growth In Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Commercial Aviation White Papers Eesi

Greenhouse Gases At Epa Greening Epa Us Epa

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
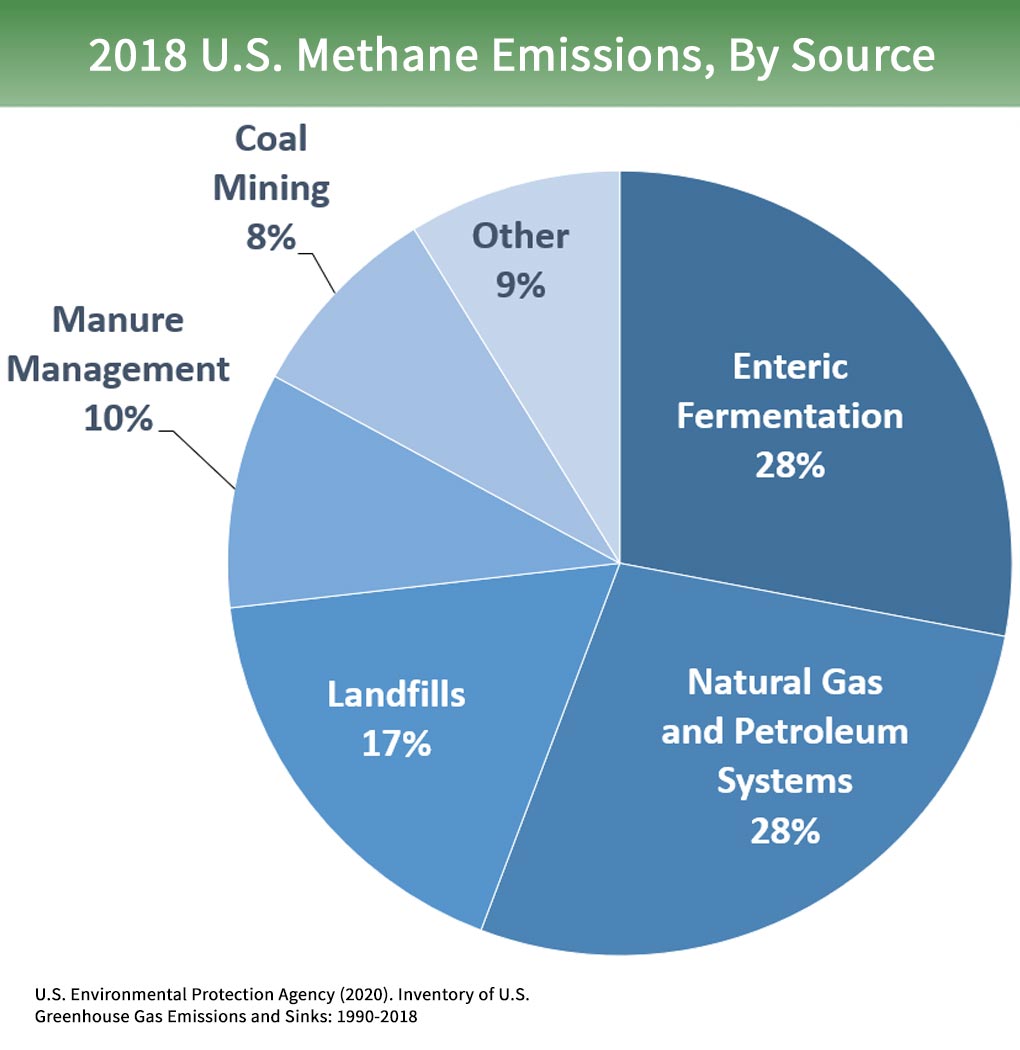
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
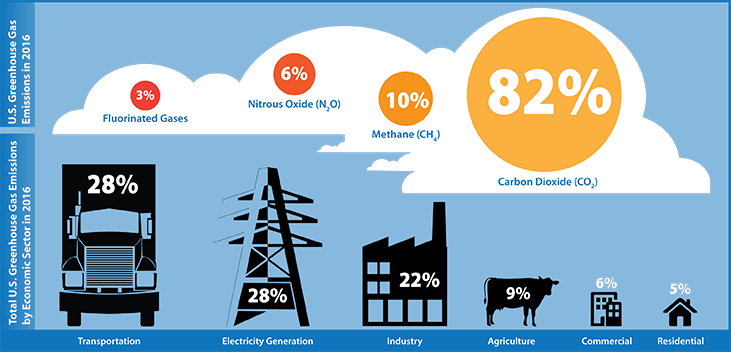
Climate Change Seia
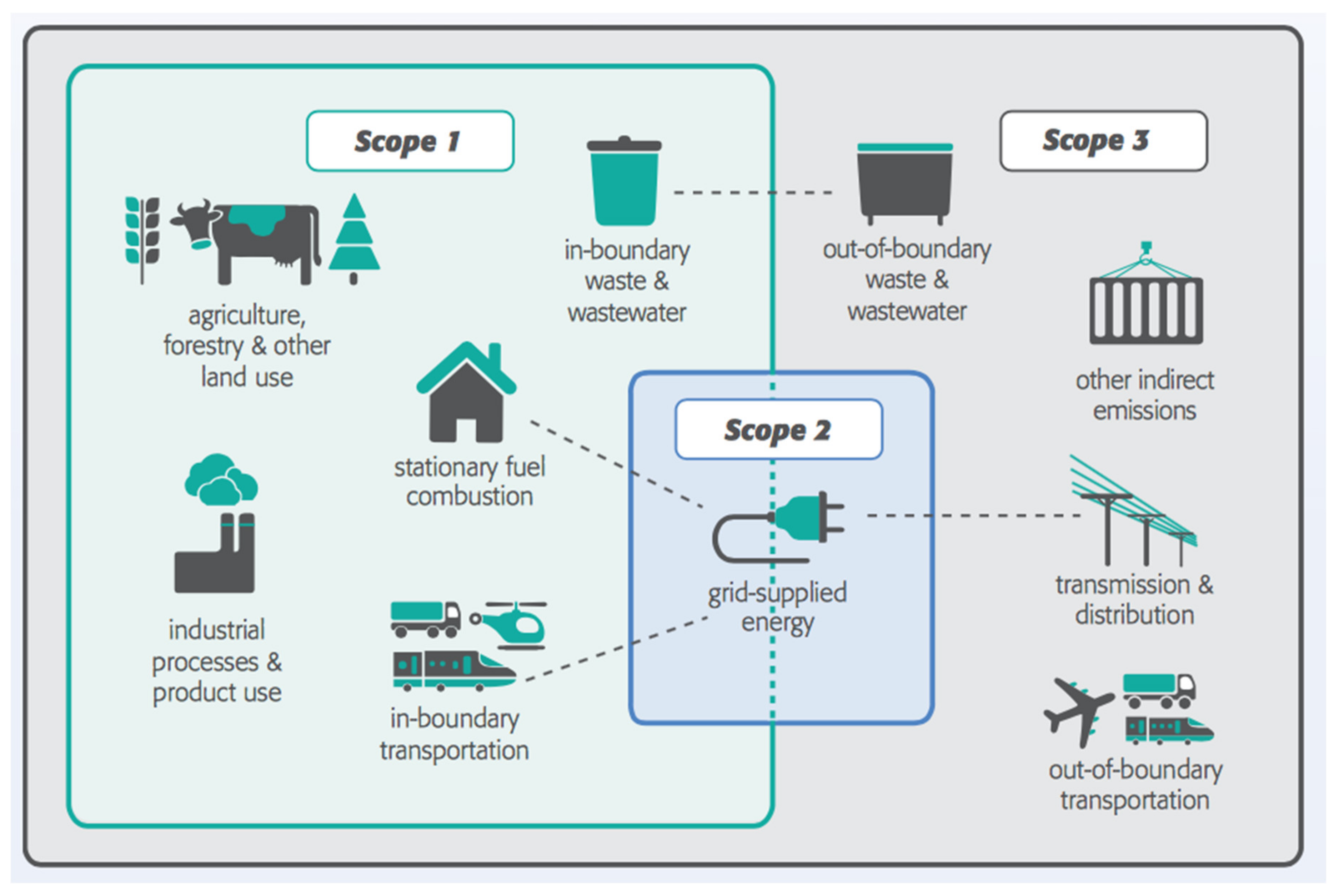
Sustainability Free Full Text Pathways To Carbon Neutral Cities Prior To A National Policy Html

Shell S Net Carbon Footprint Ambition Frequently Asked Questions Shell Global

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Sources Effects Conserve Energy Future

Scenarios For Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Surface Warming Download Scientific Diagram

Salesforce S Journey To Net Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions Salesforce Blog
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr7u2lfvmyyqcvhhgcpqag7zmbbvyplphvgcnbgwy8uaknkskoh Usqp Cau

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

Our Carbon Footprint How Do Paper Products Fit In Two Sides North America

Carbon Footprint Life Cycle Initiative

Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Carbon Offsets Reduce Emissions Climate Change

Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained

Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming

Synonyms For Greenhouse Gas Thesaurus Net
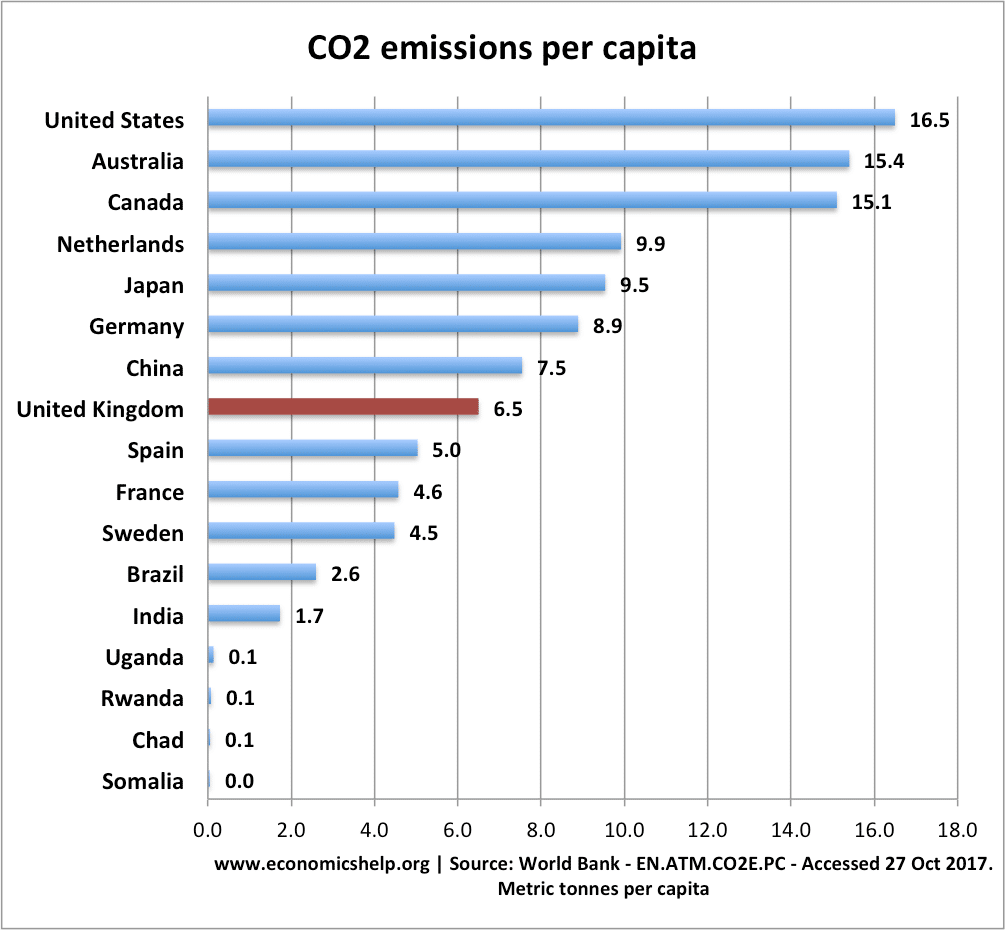
Top Co2 Polluters And Highest Per Capita Economics Help
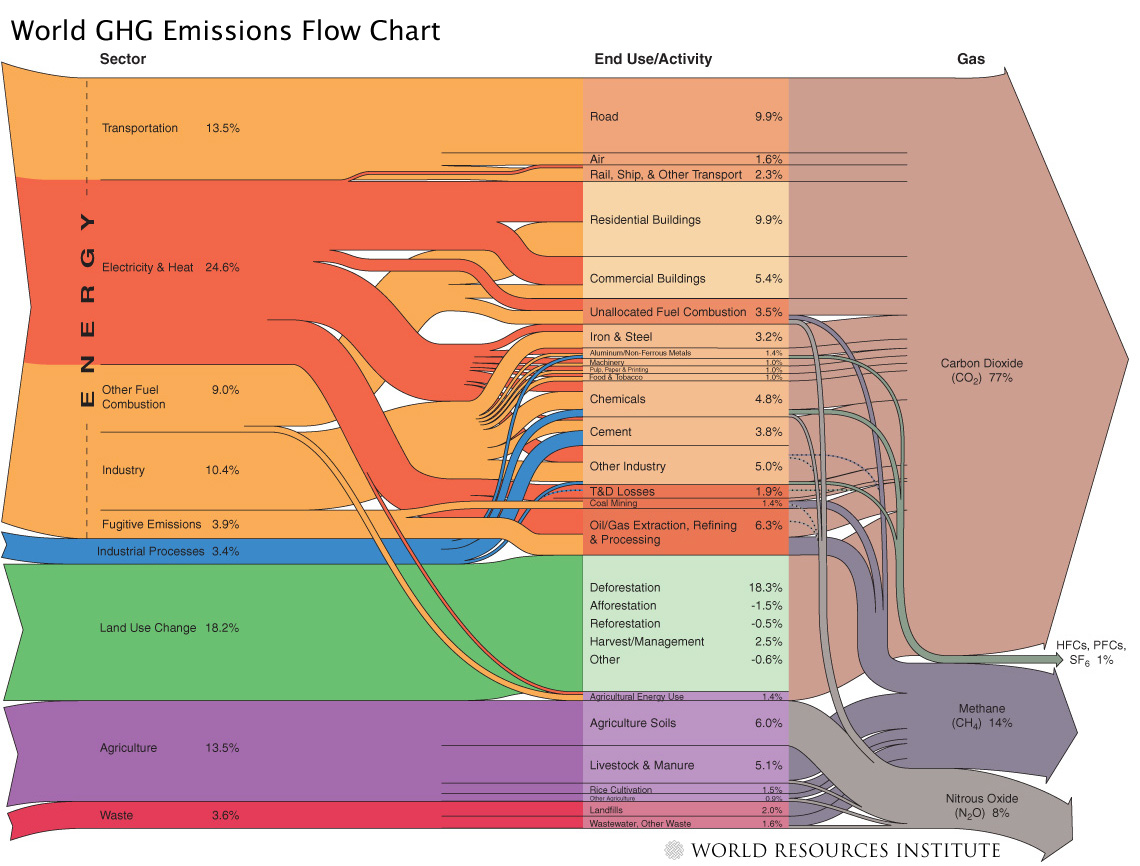
Skeptical Science Archives
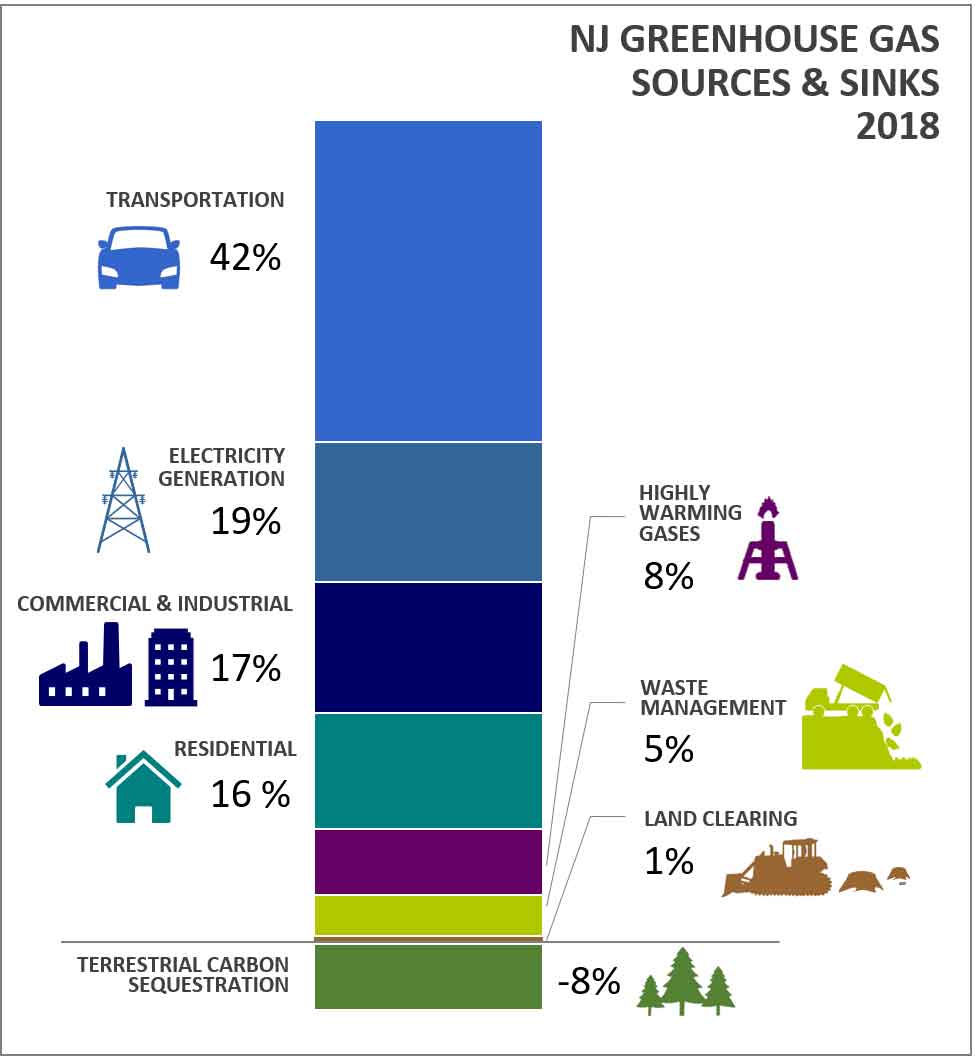
Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
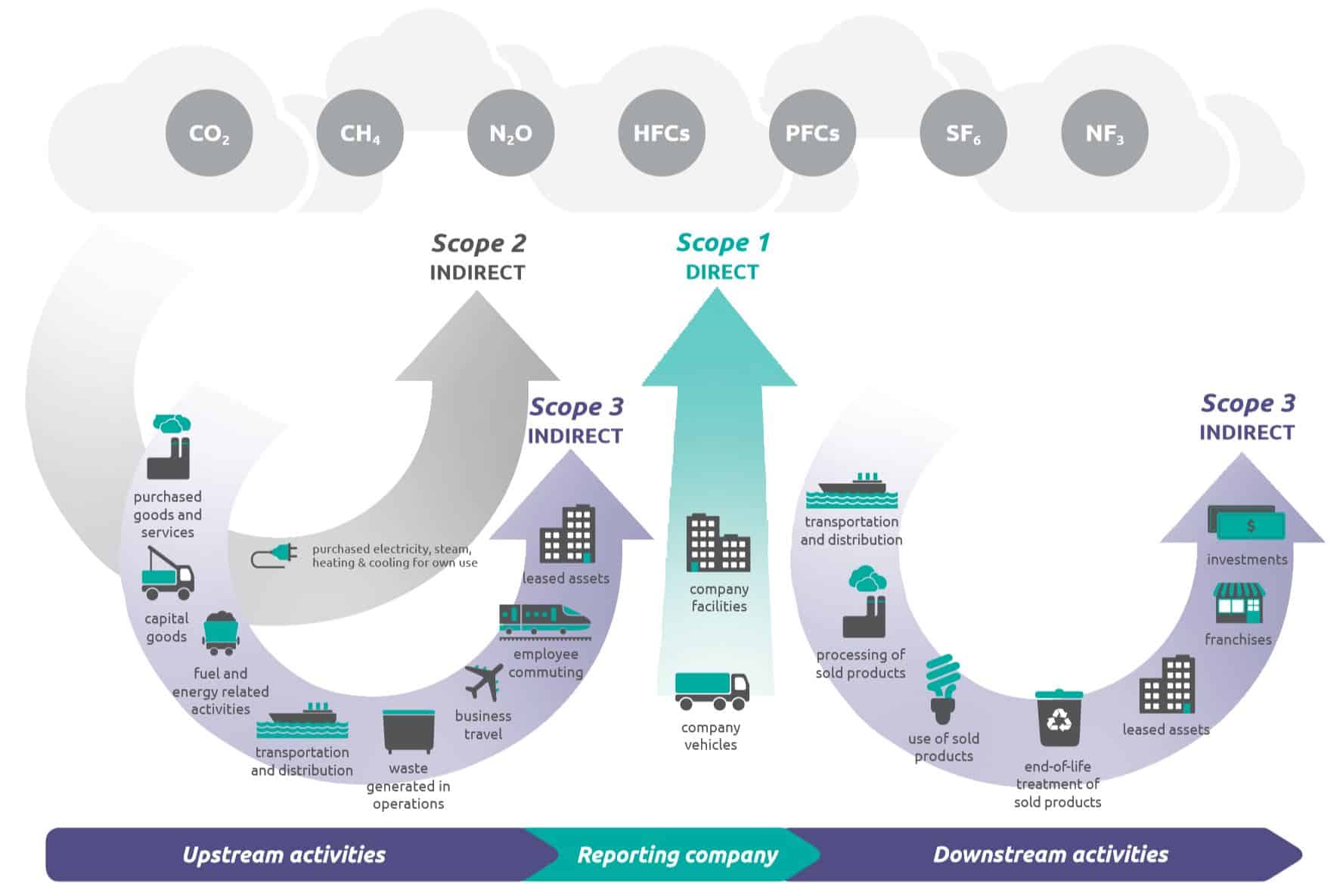
What Is The Difference Between Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Compare Your Footprint
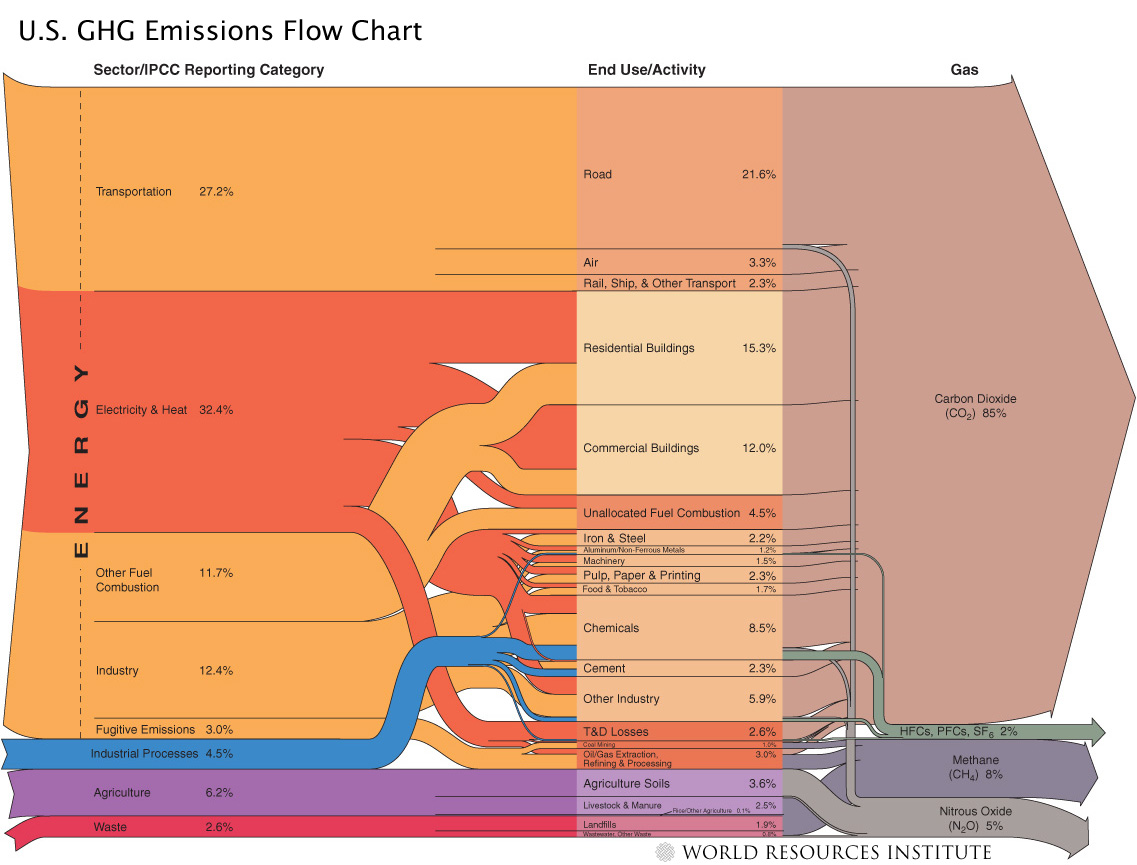
Skeptical Science Archives

Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
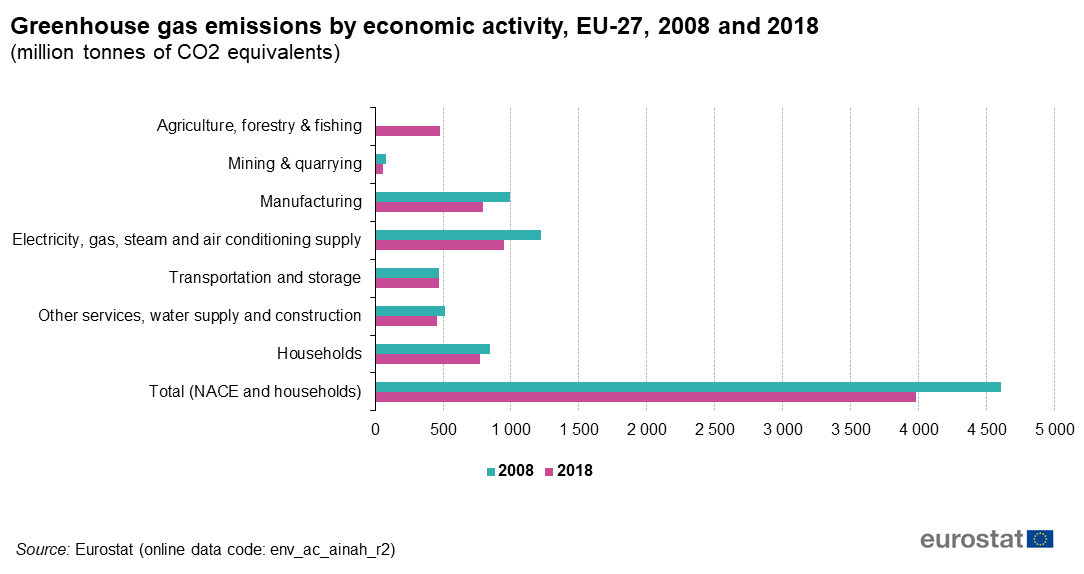
Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained
/Greenhouse-Gas-Emissions_v1.png)
Eqja5s3 Cumx8m
Dr Mat A Carbon Footprint Is Historically Defined As The Total Set Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Caused By An Individual Event Organisation Product Expressed As Co2e A Measure Of The Total Amount

Greenhouse Gases Definition Google Search In Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wastewater Treatment Plant

Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids

Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
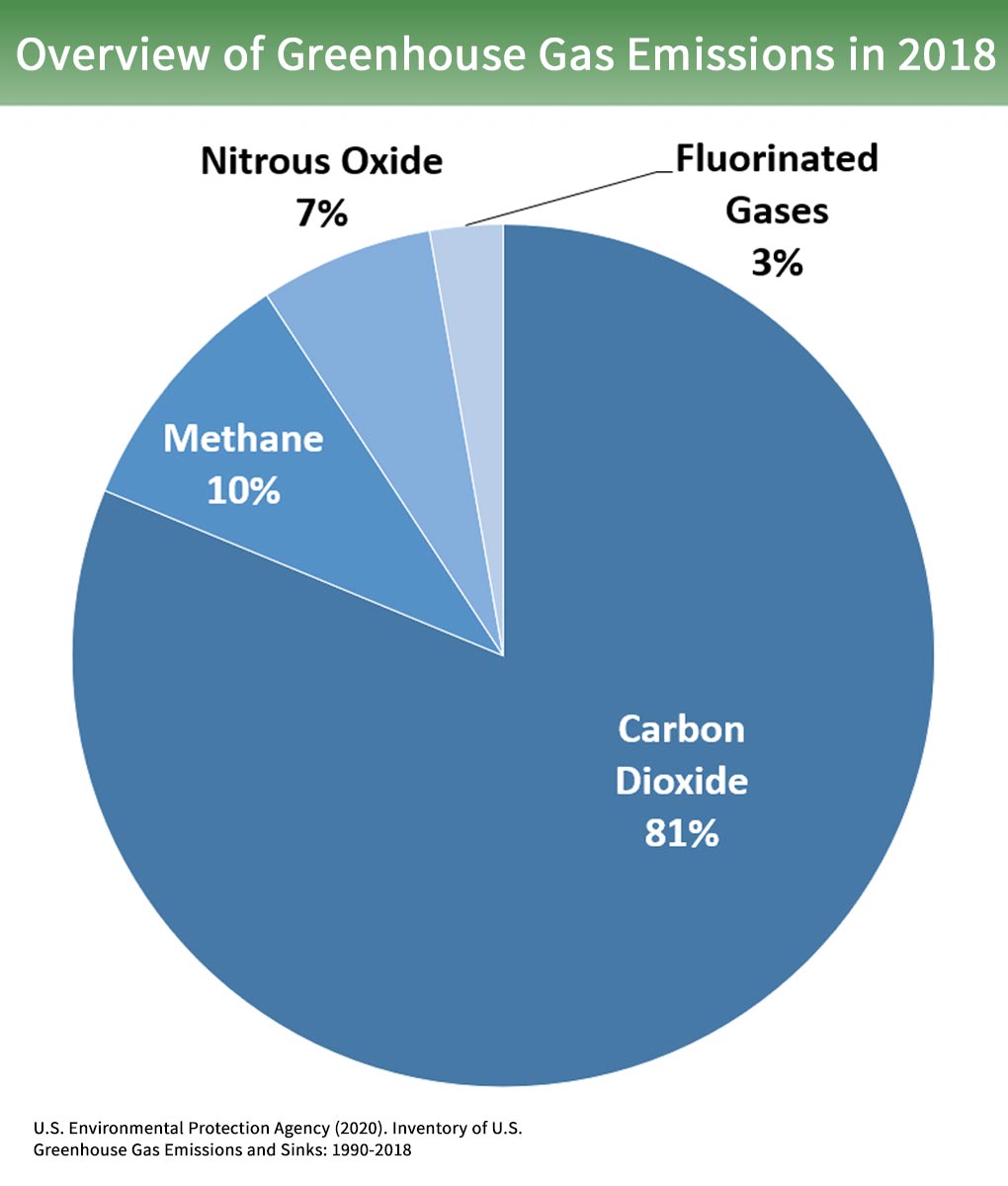
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
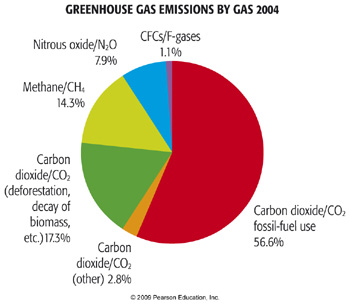
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming

Ict S Potential To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 30 Ericsson
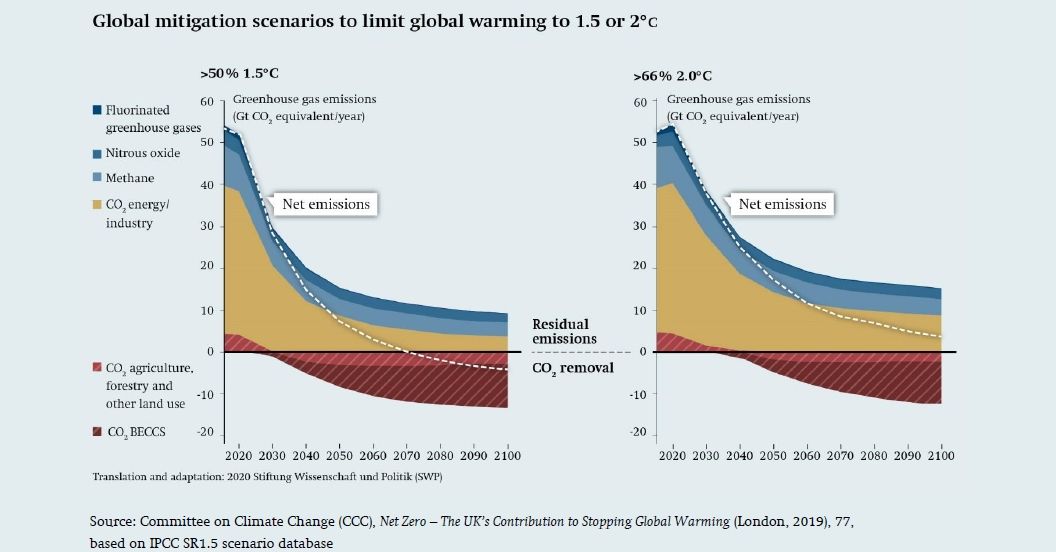
Unconventional Mitigation Swp



