Greenhouse Gases Definition Bbc Bitesize

This Is A Great Teacher Tool That They Can Use Because It Provides Different Resources On The Nonrenewable E Energy Resources Renewable Energy Resources Energy
2
Chewvalley Greenhousecms Co Uk Docs Unit 5 Changing Climate Revision Guide Pdf

Gorgon Gas Project Will Create Hundreds Of Gas Jobs While Keeping Greenhouse Gases To A Minimum Daily Green World

Gcse Bitesize Examinations Pdf Free Download
2
Physical changes in solids, liquids and gases.
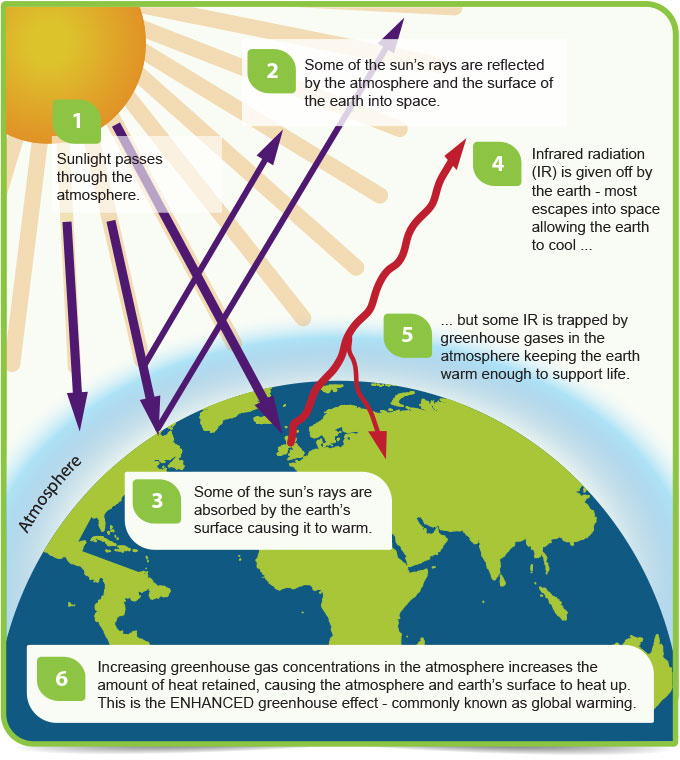
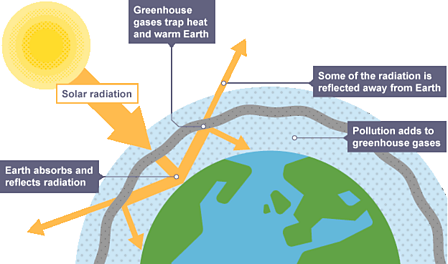
Greenhouse gases definition bbc bitesize. Earth's atmosphere is made up of gases, and these gases allow some solar radiation. Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space. Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist.
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities.In 18, CO 2 accounted for about 81.3 percent of all U.S. Absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details. Read about our approach to external linking.
Long-lived gases that remain semi-permanently in the atmosphere and do not respond physically. That’s exactly how greenhouse gases act. The greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) infrared radiation.This makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer.
Total Emissions in 18 = 6,677 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent.Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding. These gases are only a small proportion of the atmosphere but they act like a blanket by trapping some of the heat. A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range.
It's said that by the time a baby born today is 80 years old, the world will be 6 and a half degrees warmer than it is now. Greenhouse gases reflect heat radiation that the Earth emits, and stop it from being lost into space. This GCSE BBC Bitesize video is from the original programmes from 00 that were broadcast on BBC2.
The burning of fossil fuels including coal, oil, and natural gas, along with the clearing of land for agricultural use. Any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation. Most greenhouse gases are natural - water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth.
The greenhouse effect is named after the principle of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. CO2, along with a range of other greenhouse gases, is often implicated in global warming.
Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat just like the glass roof of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat. This is called the " greenhouse effect ".
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) They are all natural gases, but extra greenhouses gases can be made by humans from pollution. The Prince of Wales has warned the climate crisis will "dwarf" the impact of coronavirus. There is a powerful new satellite in the sky to monitor emissions of methane (CH4), one of the key gases driving human-induced climate change.
And according to the World Economic Forum, half of the world's tropical deforestation is illegal. Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals). Solids, liquids and gases - KS2 Science - BBC Bitesize.
Instead, greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere absorb some of the outgoing energy and return part of it to the Earth’s surface. In this way, they contribute to the greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet from losing all of its heat from the surface at night. But this new work shows that some of the declines in greenhouse gases actually cancelled each other out in terms of warming.
A) A new report has shown that greenhouse gas emissions by China will end in 10 years' time. Global warming is the rise in temperature of the earth's atmosphere. B) A new report has forecast that China will produce the world's biggest emission of greenhouse gases.
Water vapour is the most important greenhouse gas, accounting for about 98% of all warming. * Land Use, Land-Use Change, and Forestry in the United States is a net sink and offsets approximately 12 percent of these greenhouse gas emissions, this emissions offset is not included in total above. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air.
The arrival of water on. Greenhouse gases are not. That sunlight creates warmth.
While deforestation is responsible for about % of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, forests currently absorb more carbon than they emit. E-mail this page to a friend. Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century.
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid- th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. The greenhouse effect traps. The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States.
The most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are:. Greenhouse gases are gas molecules that have the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases.
But what is its role in the greenhouse effect?. They get their name from greenhouses. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;. Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. CFCs have been responsible for depleting the ozone layer as they attack and destroy ozone molecules.
Earth is much colder than the sun, but it is warmer than the space outside its atmosphere. The ozone layer is a. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases, and they.
Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed with concern. Mr Johnson said the UK's greenhouse gases were 8-10% down in on previous years. Greenhouse gases are a hot topic (pun intended) when it comes to global warming.
These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere. So changes in carbon dioxide or methane concentrations would have a relatively small impact. Nitrogen oxides from transport normally have a warming impact in the.
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth. So the greenhouse effect itself is a good thing. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
These methods of energy production emit no greenhouse gases once they are up and running. Greenhouse gases Scientists believe that the build-up of so-called greenhouse gases in the atmosphere acts like a blanket or greenhouse around the planet;. Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons.
Climate change - Climate change - Greenhouse gases:. Water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and methane. This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases.
Scientist Dr Maggie Aderin-Pocock from EADS Astrium visits the Royal Institution's new Young Scientist Centre to carry out a simple experiment that shows how CO2 traps heat. These gases absorb heat energy emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiate it back to the ground. Greenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by short-wave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longer-wavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;.
It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun. Additionally, it is used as a refrigerant. Known as Iris, the spacecraft can map plumes of CH4.
Tetrafluoromethane is a nonflammable gas that belongs to the fluorocarbon family. Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping. "The bad news is we've achieved that by sustaining an appalling economic shock in the form of.
Extra greenhouse gases are produced through activities which release carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.
What is global warming?. CF4 is a strong greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and has an atmospheric lifetime of 50,000 years. Greenhouse gases are made out of:.
Find my revision workbooks here:. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3).Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth. The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn’t let that warmth escape.
The greenhouse gas 23,500 times worse than CO2 Jump to media player Farmer Adam Twine is concerned about the little-known greenhouse gas, SF6. Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth. It covers the areas of the chemistry foundation paper.
Https://www.freesciencelessons.co.uk/workbooks In this video, we look at the Greenhouse Effect. During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Introduction.
Without the greenhouse effect the mean temperature on Earth would be -18°C and there would be very little or no life. We explore how this takes pl. In a recorded message, to be played at the virtual opening of Climate Week on Monday, Prince Charles said.
Globally it's thought deforestation is responsible for about 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Utilization of the Hall-Heroult process in aluminum production results in this gas. The wind energy produced in Denmark, for example, provides about 10 percent of the country's total energy needs.
Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun. The BBC is not responsible for the content of external sites. Carbon dioxide is an important greenhouse gas.
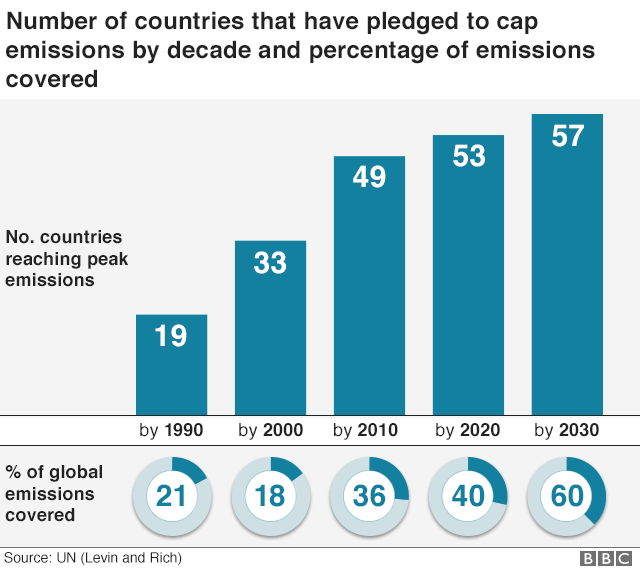
Pressure in solids and liquids. The natural greenhouse effect keeps the Earth's surface about 33C warmer than it would otherwise be. 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time.
Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town. Burning coal and petrol, known as 'fossil fuels' Cutting down of rainforests and other forests Animal waste which lets off methane. One percent of the gasses in our atmosphere , like carbon dioxide and methane, create a similar effect as a greenhouse.
Fortunately, the use of alternative energy sources, such as solar, wind, geothermal, and hydro energy, is gaining increased support worldwide. The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets.
Increasing carbon dioxide levels Humans burn fossil fuels to power cars and other machines, to generate electricity, and to keep buildings warm. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60º F colder. What are the greenhouse gases?.
The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to human activities that are adding to the warming of the atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect—the presence of gases that increases the atmosphere's retention of the heat energy of the sun. Heat is trapped inside the Earth's. This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases.
The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight.
2

Gcse Bitesize Examinations Pdf Free Download

c Bitesize Ks3 English Writing
Www Pearsonschoolsandfecolleges Co Uk Secondary Science 11 16 c Bitesize Aqa Gcse Science 9 1 Samples Digital Samples Bitesize Aqa Gcse 9 1 Combined Science Trilogy Higher Revision Guide Pdf

c Bitesize Ks3 English Writing

The Idealised Greenhouse Effect Model And Its Enemies Scienceblogs
Biogeochemical Cycles Lessons Tes Teach

Global Warming And Climate Change Homeschool Lessons In Secondary Chemistry Year 8 c Bitesize

c Bitesize English Writing A Report

Bonjour Biology Unit 3

Matter Science Homework Example July Service Tdessayqjel Eclecticpaganshop Com

The Carbon Footprint And Its Reduction Revisingscience

Deforestation And Climate Change Wikipedia
Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News

Newenergynews 03 01 10 04 01 10
Changing Climate Scotland S Environment Web

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

P2 Radiation Life c Gcse Bitesize Global Warming By Christian Tremblay Issuu

Geography Vocabulary c Bitesize

Combustion Reactions And Impact On Climate Secondary Science 4 All

c Bitesize Dyma Bynciau Bitesize Dyddiol Heddiw Here Facebook
Home Learning With c Bitesize Ks4 Geography For Year 10 c Bitesize

Geography Vocabulary c Bitesize
2

Petroleum Industry Activities And Climate Change Global To National Perspective Sciencedirect

Biofuels Biomass Bioethanol Biodiesel Biogas Comparison Of Renewable Alternative Fuels Hydrogen Gcse Chemistry Revision Notes Igcse Revising Ks4 Science

The Carbon Cycle
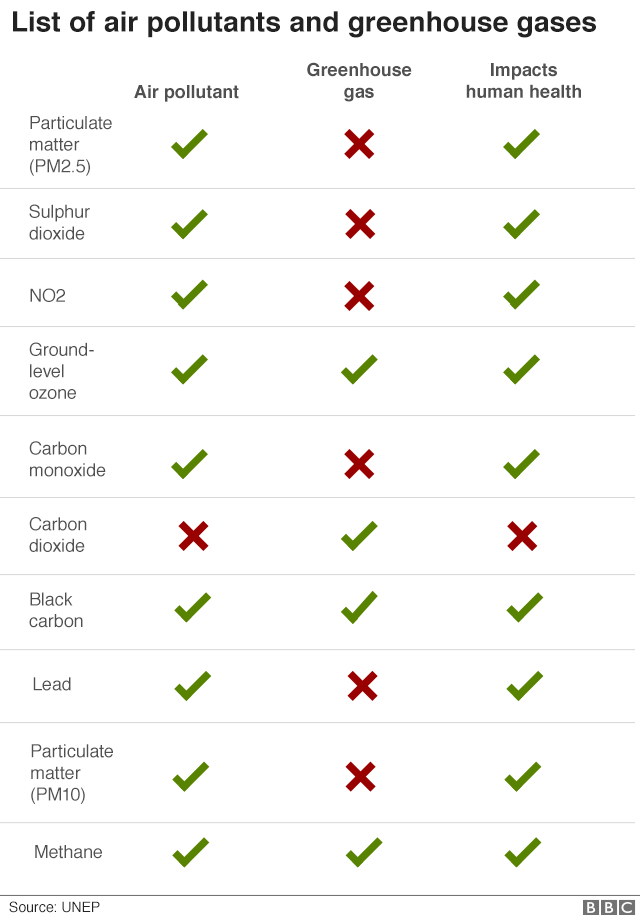
Cut Air Pollution To Fight Climate Change Un c News

Climate Change And Global Warming Climate Change Aqa Gcse Geography Revision Aqa c Bitesize

Gcse Science Revision Chemistry The Greenhouse Effect Youtube
Quiz How Much Do You Really Know About Climate Change c Bitesize
Chewvalley Greenhousecms Co Uk Docs Unit 5 Changing Climate Revision Guide Pdf

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Aren T As Bad As You Would Think Daily Green World
2
Kba Uk Portals 0 Secondary Curriculum Science Aqa 9 1 revision pack primrose kitten Pdf Ver 19 02 08 1054 493

Geography Vocabulary c Bitesize

The Greenhouse Effect The Balance Of Benefit And Risk Daily Green World
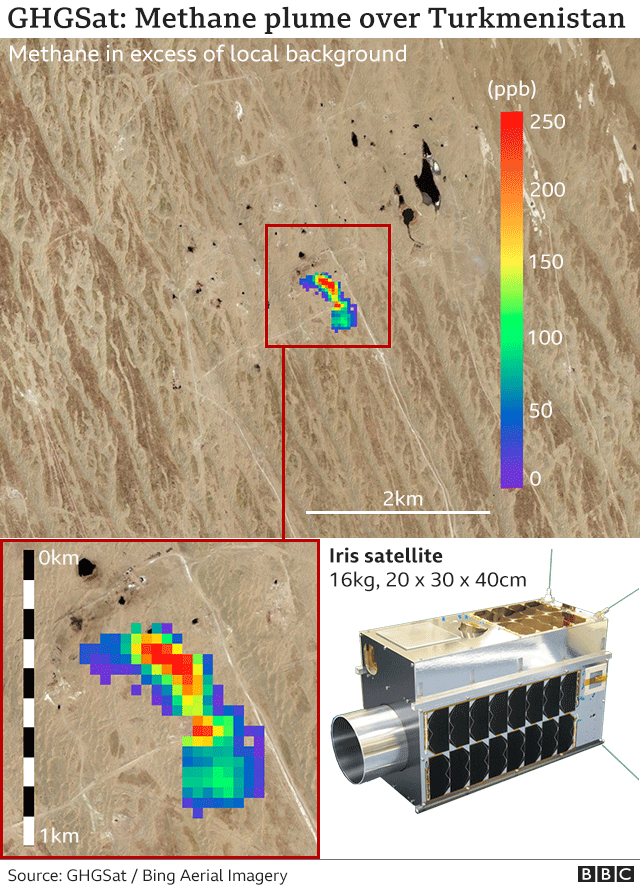
Satellite Achieves Sharp Eyed View Of Methane c News
2
Are Cities Bad For The Environment c News
Www Avonvalleycollege Org Uk S Year 8 Term 2 Knowledge Organiser Pdf
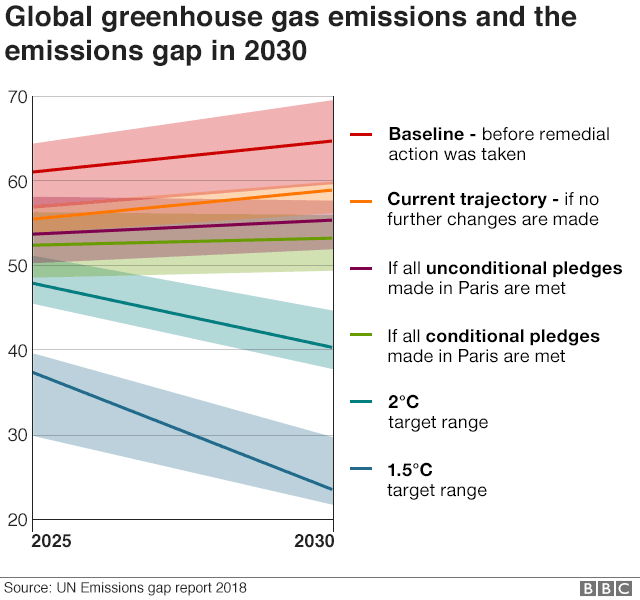
Climate Change Co2 Emissions Rising For First Time In Four Years c News

S6jvsvfyi8ovwm
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrkshs4yxsmfkaj 7o4ctqd2sjucsgee2fpvlscwmrhqroqc Usqp Cau

Portal Climate Change Wikipedia
2

Climate Change Which Vegan Milk Is Best c News

The Piggott School Year 10 Curriculum

Home Learning With c Bitesize Ks4 Geography For Year 10 c Bitesize

P2 Radiation Life c Gcse Bitesize Global Warming By Christian Tremblay Issuu

Science Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Studying Amino Amino

Application Of Software To Study The Impact Of Transportation Sectors Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction On Climate Change Kalita 16 Environmental Progress Amp Sustainable Energy Wiley Online Library

P1 P2 P3 Ocr 21 St Century Science c Bitesize Revision From c Bitesize I Want To Jump To P1 Jump To P2 Jump To P3 Start From Beginning Created By Ppt Download
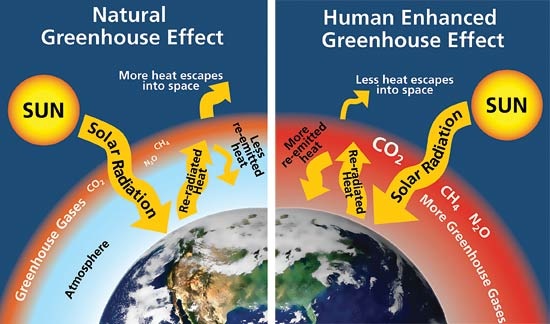
Theme 3 Economic Development And The Use Of Resources Wingate Geography
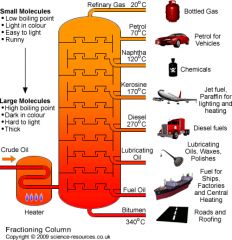
Chemistry Edexcel Igcse Flashcards Cram Com
2
2

Science Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Studying Amino Amino
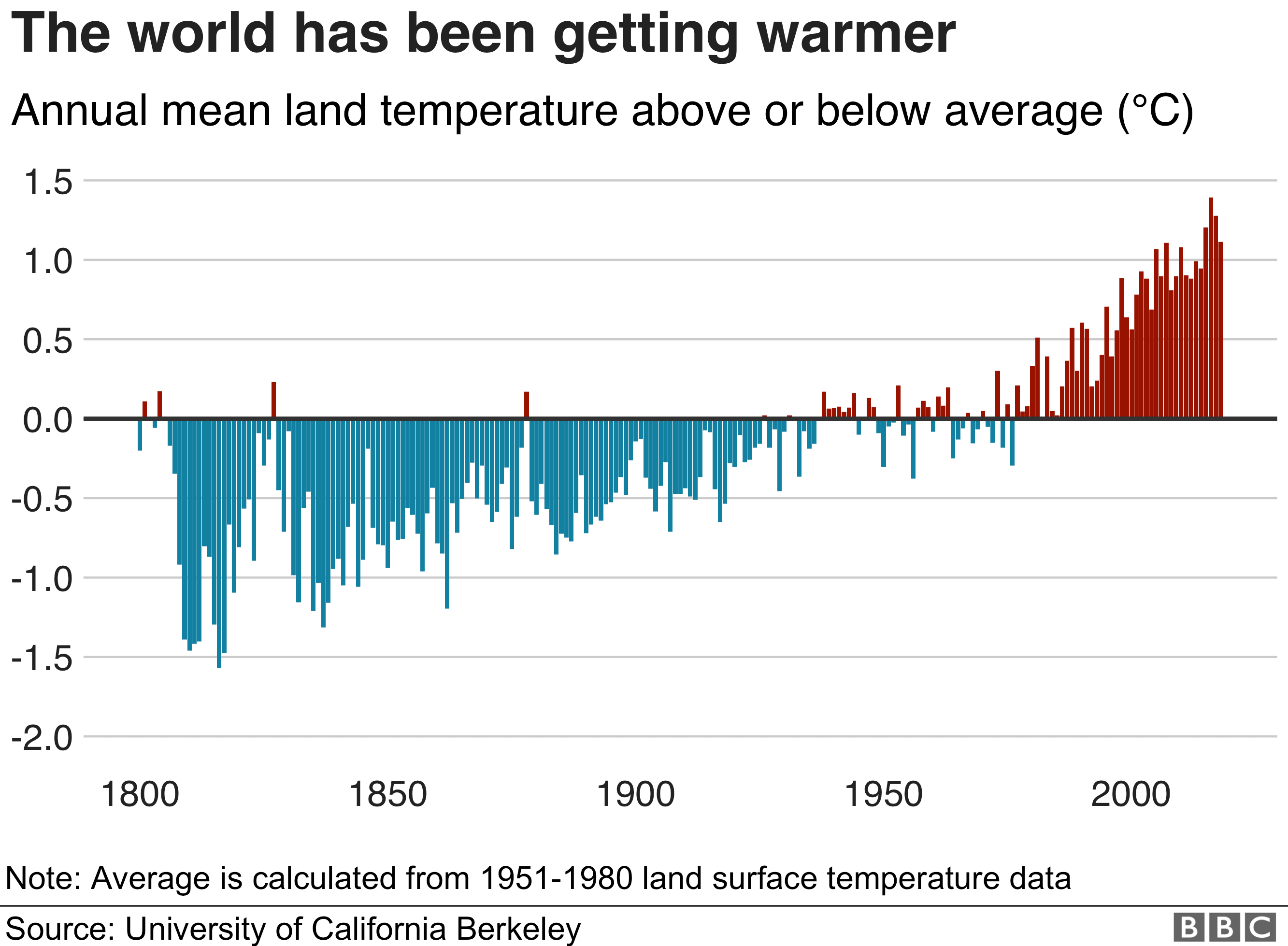
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
Www Woottonparkschool Org Uk Uploaded Knowledge Maps 19 Year 9 Knowledge Map Term 1 Pdf
Qualifications Pearson Com Content Dam Pdf Gcse Geography B 16 Teaching And Learning Materials Edexcel Gcse Geographyb Topicguide Topic1 Hazardousearth Pdf
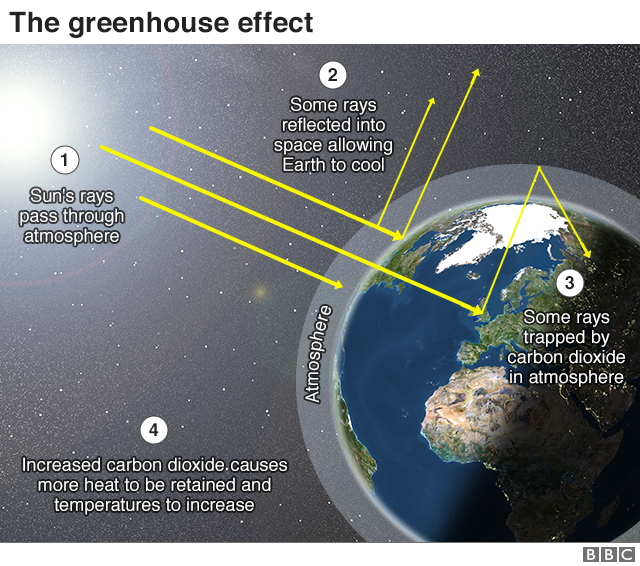
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
2

Gcse Science Revision Chemistry The Atmosphere Youtube
Mr Cartlidge Mr Cartlidge S Science Blog Page 8

Ks3 Geography Tropical Rainforest Biomes Revision 1 Geography Revision Gcse Geography Rainforest Biome

Is There Life Floating In The Clouds Of Venus c News

Year 9 Project Homework 3 As You Were Told At The Start Of This Term You Will Be Having An Exam On All Of The Work You Have Studied In Science In

Theme 3 Economic Development And The Use Of Resources Wingate Geography
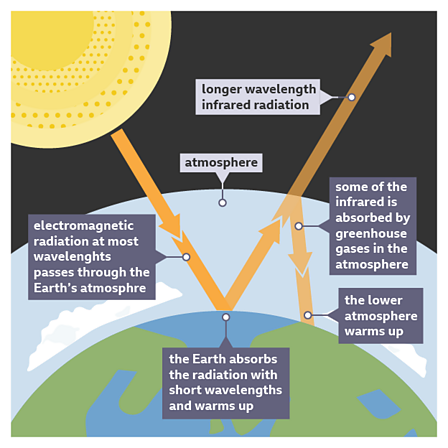
Global Warming And Climate Change Homeschool Lessons In Secondary Chemistry Year 8 c Bitesize

Nervous Syestem Revision Cards In Gcse Biology

Renewable Vs Nonrenewable Energy Resources Energy Resources Renewable Energy Resources Energy
2

Scheme Of Work Combined Science Trilogy Foundation Biology Ecology
Http Www Cambournevc Org Download Php Gcse exams overview
Energy Four Things You Will Learn From The c Briefing c Bitesize
2

Greenhouse Effect Geography 7 Omega

Gcse Bitesize Examinations Pdf Free Download

c Bitesize Back To Home Schooling Watch c Facebook

Ppt Gcse Biology Revision Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Www Magnusacademy Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 05 Geography Y7 Pdf
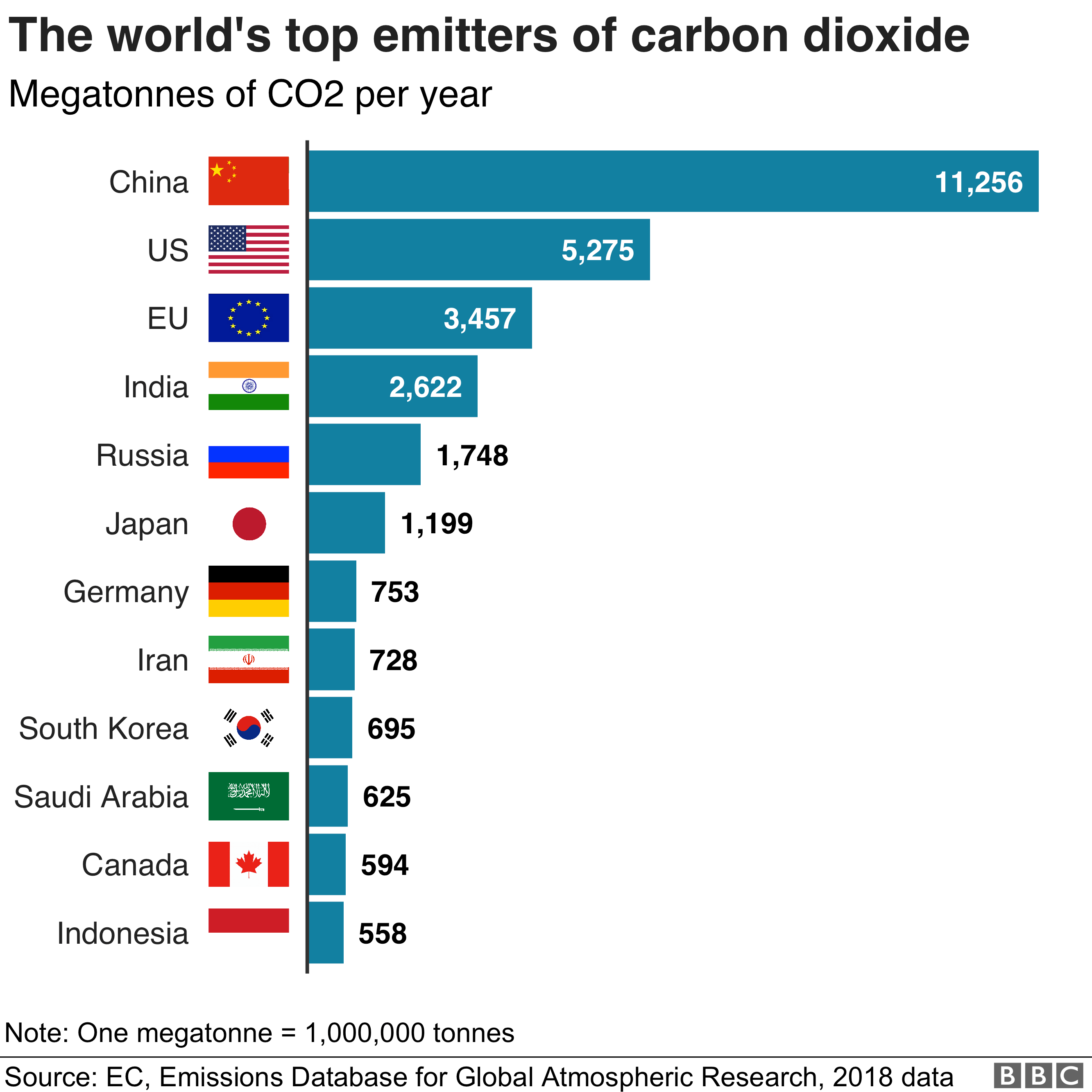
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News

Geography Vocabulary c Bitesize
Rugbyfreesecondary Co Uk Wp Content Uploads 19 07 Y8 Into Y9 Summer Reading And Activities Pdf
Arkjohnkeats Org Sites Default Files Chemistry y10 ap3 28s3 2cs5 2cs6 2cs7 29 Pdf
2

Historical Evidence Of Global Warming

Science Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Studying Amino Amino
Arkjohnkeats Org Sites Default Files Chemistry y10 ap3 28s3 2cs5 2cs6 2cs7 29 Pdf
Http Www Cambournevc Org Download Php Gcse exams overview
Http Www George Eliot Warwickshire Sch Uk Files Courses Geography Year 9 Knowledge Organisers 143

Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Lessons Tes Teach
Distribution Of Tectonic Hazards Geography Myp Gcse Dp



